what is vertigo ? cause , symptoms and treatment
Vertigo is a sensation where you feel like you or your surroundings are spinning. It is not a disease but a symptom. Many people confuse vertigo with dizziness, but they are different. Dizziness is a feeling of being lightheaded, while vertigo involves a false sense of movement.
Understanding vertigo is crucial because it affects millions of people worldwide. It can interfere with daily activities and lower the quality of life. Knowing its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage and prevent it.
This article explores the basics of vertigo. First, we explain its most common causes, such as inner ear issues or neurological conditions. Then, we cover symptoms to watch for, like nausea, balance problems, and spinning sensations. Finally, we discuss treatment options, including medical care and self-help techniques.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of vertigo. You will also learn how to seek help if you or a loved one experiences this condition. Stay informed and take the first step towards better health.
Importance of Understanding Vertigo
Understanding vertigo is essential because it affects many aspects of daily life. It is not just a minor inconvenience; for some, it can be disabling. Vertigo can make simple tasks, like walking or driving, difficult and unsafe.
Millions of people worldwide experience vertigo at some point in their lives. Knowing what causes vertigo and how to manage it can improve your quality of life. Without proper understanding, vertigo might be misdiagnosed or left untreated, leading to further complications.
By learning about vertigo, you can recognize its symptoms early. This awareness helps you seek timely treatment and avoid potential risks, such as falls or injuries. It also empowers you to support others who may be struggling with this condition.
Understanding vertigo also reduces fear and anxiety. Many people feel scared when they first experience vertigo because they don’t know what’s happening. Knowing that it is often treatable and manageable can provide reassurance and peace of mind.
In short, understanding vertigo is a step towards better health and safety. It equips you with the knowledge to handle the condition effectively and improve your well-being.
What Is Vertigo?
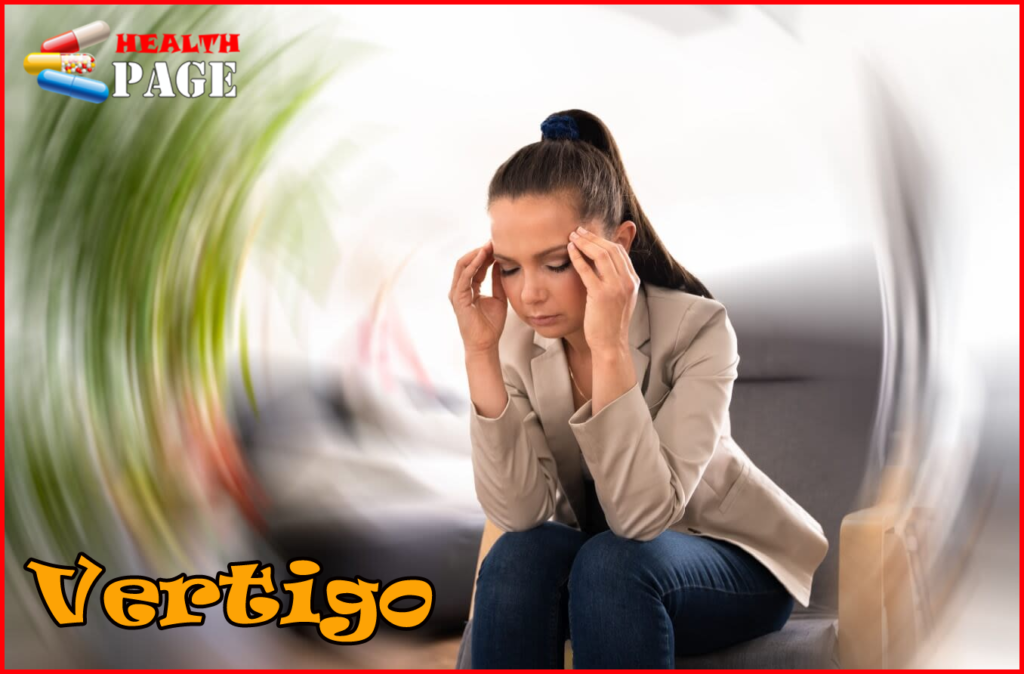

Vertigo is a medical condition where you feel like you or your surroundings are spinning. This sensation happens even when there is no actual movement. It is often caused by issues in the inner ear or brain.
Many people confuse vertigo with dizziness, but they are not the same. Dizziness is a general feeling of lightheadedness or unsteadiness. Vertigo, on the other hand, is a specific spinning or swaying sensation.
Vertigo affects the body in several ways. It can cause nausea, vomiting, and balance problems, making it hard to stand or walk. Some people experience blurred vision, headaches, or a feeling of being pulled to one side. These symptoms can disrupt daily activities and lead to falls or injuries.
Understanding vertigo helps identify its symptoms and seek proper treatment. It is important to distinguish vertigo from other conditions to ensure effective care.
Causes of Vertigo
Vertigo can arise from various underlying conditions, and understanding its causes is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Below are some common causes:
1. Inner Ear Issues
The most frequent cause of vertigo is problems in the inner ear. This area plays a crucial role in maintaining balance.
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): This occurs when tiny calcium particles in the inner ear become dislodged. These particles disrupt balance signals sent to the brain, leading to short episodes of spinning sensations.
- Meniere’s Disease: This is a chronic condition caused by fluid buildup in the inner ear. It can lead to severe vertigo episodes, hearing loss, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
2. Head or Neck Injuries
Injuries to the head or neck can damage the vestibular system, which controls balance. Whiplash or concussions often lead to vertigo. These injuries disrupt communication between the inner ear and brain, causing dizziness and disorientation.
3. Migraines
Migraines are another common cause of vertigo, especially in people with vestibular migraines. These episodes may occur with or without a headache. Symptoms include spinning sensations, nausea, and sensitivity to light or sound. Migraines often affect the brain’s ability to process balance signals, leading to vertigo.
4. Vestibular Neuritis or Labyrinthitis
These are inflammatory conditions affecting the inner ear.
- Vestibular Neuritis: Involves inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which sends balance signals to the brain.
- Labyrinthitis: Affects both the vestibular system and hearing, often caused by viral or bacterial infections. Both conditions can result in sudden, severe vertigo episodes.
5. Medications That Can Cause Vertigo
Certain medications can trigger vertigo as a side effect. Common culprits include:
- Antibiotics, such as gentamicin
- Diuretics used for high blood pressure
- Sedatives or tranquilizers
- Aspirin or high doses of anti-inflammatory drugs
These drugs may affect the inner ear or disrupt the central nervous system, leading to vertigo.
In summary, vertigo can result from various conditions, ranging from inner ear problems to medication side effects. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life.
Symptoms of Vertigo
Vertigo presents with a variety of symptoms that can disrupt daily life. Understanding these symptoms is key to identifying and managing the condition effectively. Below are the most common symptoms:
1. Spinning Sensation
The hallmark symptom of vertigo is a spinning or whirling sensation. People often describe it as feeling like they or their surroundings are moving, even when stationary. This false sense of motion can range from mild to severe and may last for a few seconds, minutes, or even hours. It is often triggered by head movements or changes in position, such as lying down or looking up.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a frequent companion of vertigo. The spinning sensation disrupts the brain’s ability to process balance signals, causing queasiness. In more severe cases, this nausea may escalate to vomiting, further worsening discomfort. These symptoms can make eating or drinking difficult during an episode of vertigo.
3. Balance Problems
Vertigo often interferes with the ability to maintain balance. Individuals may feel unsteady or as if they are being pulled to one side. This instability increases the risk of falls, especially in older adults. Everyday activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even standing still, become challenging.
4. Hearing Loss or Ringing in the Ears
Some types of vertigo, such as those associated with Meniere’s disease, can cause hearing issues. These include partial or temporary hearing loss and tinnitus, a ringing, buzzing, or roaring sound in the ears. These symptoms may occur alongside vertigo or independently, depending on the underlying cause.
5. Sweating
Excessive sweating is another symptom often experienced during a vertigo episode. It is typically a result of the body’s response to dizziness and disorientation. Sweating may occur suddenly and be accompanied by paleness or a clammy feeling.
How These Symptoms Affect Daily Life
These symptoms can be distressing and interfere with normal activities. For instance, balance problems and spinning sensations make it difficult to walk or drive. Nausea and vomiting can lead to dehydration, while hearing issues may impact communication.
Recognizing these symptoms and seeking medical advice is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life and reduce the impact of vertigo on daily routines.
Diagnosis of Vertigo
Diagnosing vertigo requires a detailed evaluation to determine its cause. Medical professionals use various methods, including medical history reviews, physical exams, and diagnostic tests. Below are the key steps involved in diagnosing vertigo:
1.

Medical History Review
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history. Doctors ask about the onset, duration, and frequency of vertigo episodes. They may inquire about associated symptoms like nausea, hearing loss, or balance problems. Questions about previous ear infections, head injuries, or family history of similar conditions help identify potential causes. Information about current medications is also critical since some drugs can trigger vertigo as a side effect.
2. Physical Examination
A physical exam helps evaluate balance and coordination. Doctors often perform specific maneuvers, like the Dix-Hallpike test, to provoke vertigo symptoms. This test involves moving the head and body in certain ways to observe eye movements, which can indicate inner ear issues. Observing unsteady walking patterns or difficulty standing also provides valuable clues.
3. Hearing Tests
Hearing tests, such as audiometry, are commonly used when vertigo is suspected to involve the inner ear. These tests measure hearing ability and can identify conditions like Meniere’s disease, which causes hearing loss and vertigo. Assessing hearing also helps rule out other potential issues unrelated to vertigo.
4. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans may be necessary in some cases. These scans provide detailed images of the brain and inner ear structures. They are especially useful for ruling out serious causes of vertigo, such as tumors, strokes, or multiple sclerosis. Imaging is typically recommended when symptoms are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other neurological signs.
5. Vestibular Tests
Specialized vestibular tests evaluate the inner ear’s function, which controls balance. Common tests include:
- Electronystagmography (ENG): Measures involuntary eye movements in response to stimuli.
- Rotational Chair Test: Assesses how the inner ear responds to head movements.
- Posturography: Analyzes balance while standing on different surfaces.
Treatment Options for Vertigo
Treating vertigo depends on its cause and severity. Various approaches, from medications to lifestyle changes, can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Below are the main treatment options:
1. Medications
Medications are often prescribed to relieve vertigo symptoms. Common types include:
- Antihistamines: Such as meclizine or dimenhydrinate, which reduce dizziness and spinning sensations.
- Anti-nausea drugs: Like promethazine, to alleviate nausea and vomiting associated with vertigo.
- Diuretics: Used in conditions like Meniere’s disease to reduce fluid buildup in the inner ear.
- Corticosteroids: Help reduce inflammation in cases of vestibular neuritis or labyrinthitis.
Medications provide short-term relief but may not address the underlying cause, making them a temporary solution.
2. Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT)
VRT is a specialized form of physical therapy designed to improve balance and reduce dizziness. A therapist guides patients through exercises that retrain the brain to adapt to inner ear imbalances. VRT is highly effective for conditions like vestibular neuritis, where balance problems persist after the initial episode of vertigo.
3. Canalith Repositioning Procedures
For vertigo caused by Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV), canalith repositioning procedures are highly effective. The most common method is the Epley maneuver, where a healthcare provider moves the patient’s head through specific positions. These movements help dislodge calcium particles in the inner ear and reposition them, reducing symptoms almost immediately.
4. Surgery (in Severe Cases)
Surgery is a rare treatment option reserved for severe cases of vertigo that don’t respond to other therapies. Examples include:
- Labyrinthectomy: Removes the inner ear on the affected side.
- Vestibular nerve section: Cuts the nerve transmitting balance signals from the affected ear to the brain.
Surgery is usually considered only when vertigo is debilitating and caused by conditions like Meniere’s disease.
5. Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Lifestyle adjustments can help manage vertigo effectively. These include:
- Avoiding sudden head movements or positions that trigger symptoms.
- Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet low in salt for Meniere’s disease.
- Practicing relaxation techniques to reduce stress, which can worsen vertigo.
- Using home remedies like ginger tea to alleviate nausea.
Managing Vertigo at Home
Managing vertigo at home involves creating a safe environment, practicing simple exercises, and adopting healthy habits. These strategies can help reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life. Below are some effective ways to manage vertigo at home:
1. Create a Safe Home Environment
A safe home environment is essential to prevent injuries caused by falls or imbalance during vertigo episodes.
- Remove tripping hazards like loose rugs, clutter, or exposed wires.
- Install grab bars in bathrooms and along stairways for added support.
- Use non-slip mats in areas prone to wetness, such as the kitchen or bathroom.
- Ensure proper lighting throughout your home to reduce disorientation in dark spaces.
Having someone nearby during severe episodes can also provide extra safety and assistance.
2. Gentle Exercises and Activities
Engaging in gentle exercises can help improve balance and reduce vertigo symptoms over time.
- Head and neck movements: Gradually turning your head or nodding can train your brain to adapt to motion-related dizziness.
- Tai Chi or yoga: These activities promote balance and relaxation.
- Vestibular exercises: Specific movements prescribed by a healthcare professional, such as the Brandt-Daroff exercise, can relieve symptoms of BPPV.
Avoid strenuous activities or rapid head movements, as they might worsen symptoms.
3. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can worsen vertigo symptoms, so staying hydrated is crucial.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol, as they can affect the inner ear and exacerbate symptoms.
- For individuals with Meniere’s disease, limit salt intake to prevent fluid buildup in the inner ear.
Proper hydration supports overall health and minimizes triggers that can lead to vertigo.
4. Practice Stress Management Techniques
Stress and anxiety can intensify vertigo episodes. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help manage stress.
- Deep breathing exercises: Inhale slowly through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale through your mouth.
- Meditation or mindfulness: Focus on the present moment to calm your mind.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Tense and release different muscle groups to reduce physical tension.
Prioritize adequate sleep and engage in hobbies to reduce stress levels naturally.
Preventing Vertigo
While vertigo may not always be completely preventable, there are several steps you can take to reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. By avoiding known triggers, maintaining regular check-ups, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can manage vertigo more effectively. Here are some key strategies for preventing vertigo:
1. Avoid Known Triggers
Many vertigo episodes are triggered by specific activities or conditions. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help prevent future occurrences.
- Head movements: Rapid head turns or tilting the head back can trigger vertigo, especially in people with conditions like Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). Try to move slowly and carefully, especially when getting out of bed or standing up.
- Bright lights or loud noises: For those with vestibular migraines or Meniere’s disease, exposure to bright lights or loud sounds can trigger vertigo. Minimize exposure to such environments when possible.
- Certain positions: In BPPV, specific head positions can lead to vertigo. Avoid lying flat on your back or looking up for prolonged periods.
By understanding what sets off your vertigo, you can better manage your environment and reduce your risk of triggering symptoms.
2. Regular Check-ups with Healthcare Provider
Routine visits to your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your condition, especially if you have an ongoing issue with vertigo.
- Early detection of underlying conditions: Regular check-ups allow for early diagnosis and management of any underlying conditions that could contribute to vertigo, such as Meniere’s disease, ear infections, or vestibular disorders.
- Monitor changes in symptoms: Keeping track of any changes in vertigo symptoms helps your doctor adjust treatment plans or recommend new therapies.
- Hearing and balance tests: Regular hearing and balance evaluations can help detect any issues before they worsen.
Staying on top of your health with regular check-ups ensures that vertigo remains manageable and doesn’t become a long-term issue.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle plays a significant role in preventing vertigo.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity, especially balance exercises, strengthens muscles and helps improve coordination. Activities like walking, yoga, and tai chi can help you maintain good balance.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can make vertigo worse. Regular relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or journaling, can help reduce stress levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking affects circulation and can impair ear function, increasing the risk of vertigo.
By focusing on your overall health, you can reduce the likelihood of vertigo episodes and enjoy a higher quality of life.
4. Proper Hydration and Diet
A balanced diet and proper hydration are essential for maintaining optimal inner ear function.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can trigger dizziness and vertigo. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit salt intake: High salt consumption can cause fluid buildup in the inner ear, leading to Meniere’s disease. A low-sodium diet helps keep fluid levels balanced.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: Include foods high in antioxidants and essential vitamins to support your overall health and prevent vertigo symptoms.
By adopting a well-balanced diet and staying hydrated, you can support your body’s ability to manage vertigo triggers.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of vertigo are mild and resolve on their own, there are times when medical intervention is necessary. It’s important to know when to seek help from a healthcare provider to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment. Below are some key situations when you should see a doctor:
1. Persistent Symptoms
If vertigo symptoms last longer than a few days or occur frequently, it’s essential to consult a doctor. Persistent vertigo may indicate an underlying condition that needs medical attention, such as vestibular disorders or Meniere’s disease. Continuous symptoms can also lead to chronic imbalance, making it difficult to perform daily tasks. A healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, conduct appropriate tests, and recommend treatment options to alleviate the condition.
2. Severe Symptoms Affecting Daily Life
If vertigo is severe enough to interfere with your daily activities, it is time to see a doctor. Severe vertigo can lead to significant difficulties with basic functions like walking, driving, or even standing. In these cases, vertigo can cause accidents or falls, leading to injuries. Additionally, if vertigo is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or a constant feeling of unsteadiness, it can severely affect your quality of life. A doctor can help manage these severe symptoms and provide strategies to reduce their impact on your routine.
3. Unexplained Hearing Loss
Vertigo combined with sudden or unexplained hearing loss is a warning sign that requires immediate medical attention. Conditions like Meniere’s disease, vestibular neuritis, or even infections can cause both vertigo and hearing loss. Any sudden or gradual hearing changes, particularly if they occur alongside vertigo, should not be ignored. A doctor may perform hearing tests and other diagnostic procedures to identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment to prevent further damage.
4. Sudden Onset of Vertigo
If vertigo comes on suddenly, particularly if it is severe or accompanied by other symptoms like difficulty speaking, numbness, or weakness, seek medical help immediately. Sudden vertigo, especially when combined with neurological symptoms, could indicate a more serious condition such as a stroke or a brain injury. These medical emergencies require immediate intervention to prevent further complications. If you experience sudden vertigo with any concerning symptoms, go to the emergency room or contact a healthcare provider right away.
Conclusion
Vertigo is a condition characterized by a spinning sensation that can disrupt daily life. It is often caused by inner ear issues, head injuries, migraines, or infections. The key symptoms of vertigo include dizziness, nausea, balance problems, hearing loss, and sweating. Diagnosing vertigo involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, hearing tests, and sometimes imaging or vestibular tests. Treatment options vary depending on the cause, with medications, vestibular rehabilitation therapy, and canalith repositioning procedures being common approaches. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Preventing vertigo involves avoiding known triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and scheduling regular check-ups with a healthcare provider. Managing vertigo at home through a safe environment, gentle exercises, and stress management techniques can help reduce symptoms.
It is important to seek professional medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, unexplained hearing loss, or sudden onset of vertigo. Medical intervention can help identify the cause and provide the appropriate treatment to prevent further complications.
If you are experiencing vertigo symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of vertigo on your daily routine. Taking the necessary steps to manage vertigo can help you regain balance and confidence in your daily activities.


Pingback: When can you drink best protein powder to get the best bodybuilding performance?
Pingback: What is hypertension ? Early and late symptoms
Pingback: Head Impulse Test: Procedure, Uses & Vestibular Function Guide
Pingback: 7 Surprising Facts About BPV ICD-10 That Save Your Health