What are the symptoms of whooping cough? Can whooping cough in children be cured?
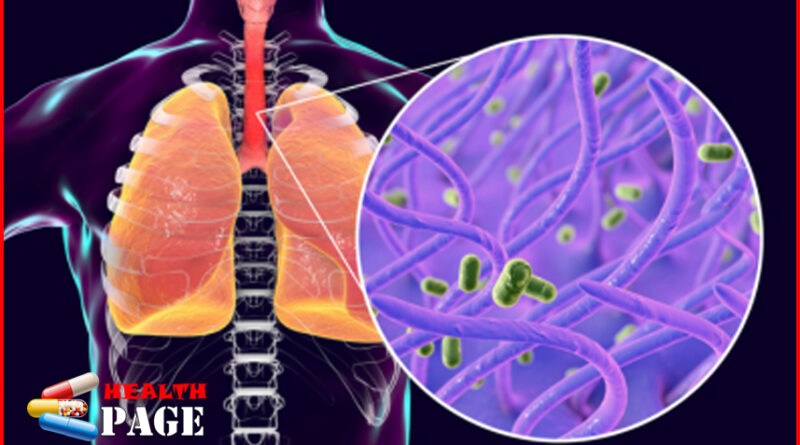
Whooping cough is a respiratory disease caused by Bordetella pertussis. It is called pertussis because of the paroxysmal cough that lasts for 2-3 months. It is a highly contagious disease.
Whooping cough is an acute respiratory disease mainly caused by infection with Bordetella pertussis. When severe coughing occurs, it is often accompanied by high-pitched inhalation sounds and other phenomena.

Bordetella pertussis infection causes whooping cough
The course of whooping cough can last for several months. The main route of transmission of the disease is through droplets . Bordetella pertussis is an oval, short rod that belongs to the Gram-negative bacteria group.
So what are the common symptoms of whooping cough?
1. Low-grade fever
Whooping cough is accompanied by fever symptoms in the early stages, and most cases are low-grade fever, with body temperature often fluctuating between 37.3℃-38℃. In the later stages, the fever or feverish state will subside.
2. Mild cough
The typical symptom of whooping cough is coughing, which is accompanied by mild single coughs in the early stage, but as time goes by, the cough will become more severe and obvious paroxysmal and spasmodic coughs will appear.
3. Nasal congestion and runny nose
In the early stages of infection with Bordetella pertussis, symptoms similar to the common cold are likely to occur, such as sneezing, runny nose, and nasal congestion.
4. Sore throat
Whooping cough can cause the throat to become dry, especially at night when the dryness is more obvious, and may even cause sputum and throat pain.
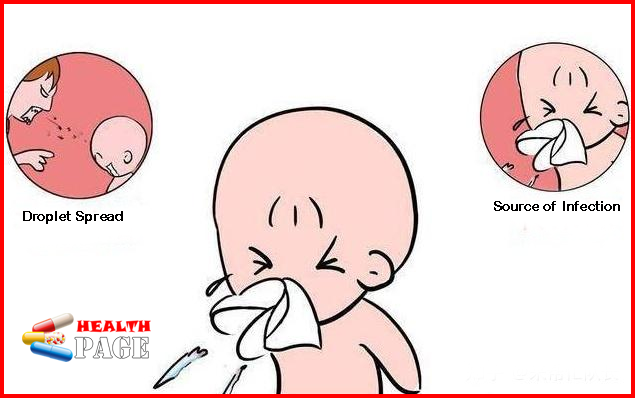
The course of whooping cough is long. Treating the course and symptoms accordingly will help to quickly recover from the disease.
According to the course of the disease, it can generally be divided into three situations.
1. Catarrhal stage
The initial symptoms after bacterial infection are mainly paroxysmal spasmodic coughing, sneezing, and low fever. Generally, the symptoms may last for 7 to 10 days .
2. Spasmodic cough stage
During the spasmodic cough period, obvious paroxysmal and spasmodic coughs may occur. The symptoms of the children are often manifested by red face and cyanosis of lips, tongue protruding outward, anxious expression, bent body, or severe coughing may cause facial edema, red bloodshot conjunctiva, and nose bleeding in the later stage. It is easily triggered by eating, cold, smoke stimulation, crying, emotional excitement, etc., and generally lasts for 2 to 6 weeks , and can last for more than 2 months .
3. Recovery period
During the recovery period, the cough symptom gradually weakens, and other symptoms such as fever and nasal congestion subside. The recovery period is about 2 to 3 weeks . However, complications such as bronchopneumonia , emphysema and other diseases may linger and last for months or even longer.

Whooping cough is a contagious disease that is mainly prevented through vaccination, but can whooping cough in children be cured?
If detected and treated early , most cases of whooping cough can be cured. Active use of corresponding sensitive antibiotics in the early stages of the disease and active relief of symptoms can promote recovery as soon as possible.
However, because the children are too young or their conditions are already serious and accompanied by multiple complications involving the respiratory system, the children’s lives and health may be endangered . Most of the cases are in the early stages of the disease and are relatively mild, so active treatment has a better prognosis and can even lead to a complete cure.
Whooping cough generally has a long course of illness. Children with the disease and their families should follow the doctor’s orders and use medications appropriately . They should not stop taking medications at will. At the same time, during treatment, they should reduce contact with pathogens, reduce recurrences of the disease, and facilitate recovery.
What should children with whooping cough generally pay attention to?
Bordetella pertussis is an infectious bacterium, so the treatment of pertussis is mainly divided into cause treatment and symptomatic treatment.
1. Cause treatment
Antimicrobial drugs are mainly used for antibacterial treatment, such as commonly used macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin, roxithromycin, azithromycin and other antibiotics, cephalosporins such as cephalexin, cefadroxil, cefazolin and other antibiotics, which can effectively inhibit the reproduction and growth of pathogens and are conducive to the recovery of the disease.
2. Symptomatic treatment
Cough suppressants are mainly used for cough suppression, such as inhaled nebulizer drugs such as budesonide , ipratropium bromide , salbutamol , etc. to relieve children’s cough symptoms, or Western medicine is used for cough suppression. Common Western medicine cough suppressants include ambroxol , ambroxol hydrochloride , etc., as well as Chinese patent medicine preparations for cough suppression and expectoration. Commonly used medicines include Feili Ke mixture , compound fresh bamboo sap liquid , etc.

The most effective way to treat whooping cough is to fight infection. What else should we pay attention to when treating children with whooping cough?
1. Proper isolation
Whooping cough is a highly contagious disease , so the patient needs to be isolated and daily care should be carried out to avoid complications. Blood pressure and heart rate should be monitored at all times during treatment. In addition, you must follow the doctor’s orders and use antibiotics correctly.
2. Chinese medicine can be used as an auxiliary treatment in the later stage
Some Chinese medicinal materials can also assist in regulating the body. Such as using Chinese herbal decoctions such as Xiaoqinglong Decoction , Sangbaipi Decoction, Ginseng and Schisandra Decoction to clear the lungs and resolve phlegm, relieve gas and relieve cough, or using medicinal diet therapy such as Houttuynia cordata boiled eggs , honey boiled eggs, etc. to moisten the lungs and resolve phlegm and relieve cough symptoms.

To prevent whooping cough, vaccination is the most effective means. At the same time, the source of infectious bacteria must be controlled. For example, during epidemics, gatherings in public places should be reduced. In particular, patients with whooping cough must be treated and isolated in a timely manner.
At the same time, you should pay attention to ensuring the ventilation of the house, and disinfect it in time if you cough up phlegm. In addition, you should enhance your own immunity and reduce contact with pathogens.
In conclusion:
Family members of children with whooping cough should ensure the children’s mental health during the period of self-isolation, have the children wear masks in time to reduce the infection rate, and pay attention to disinfection of the items used.