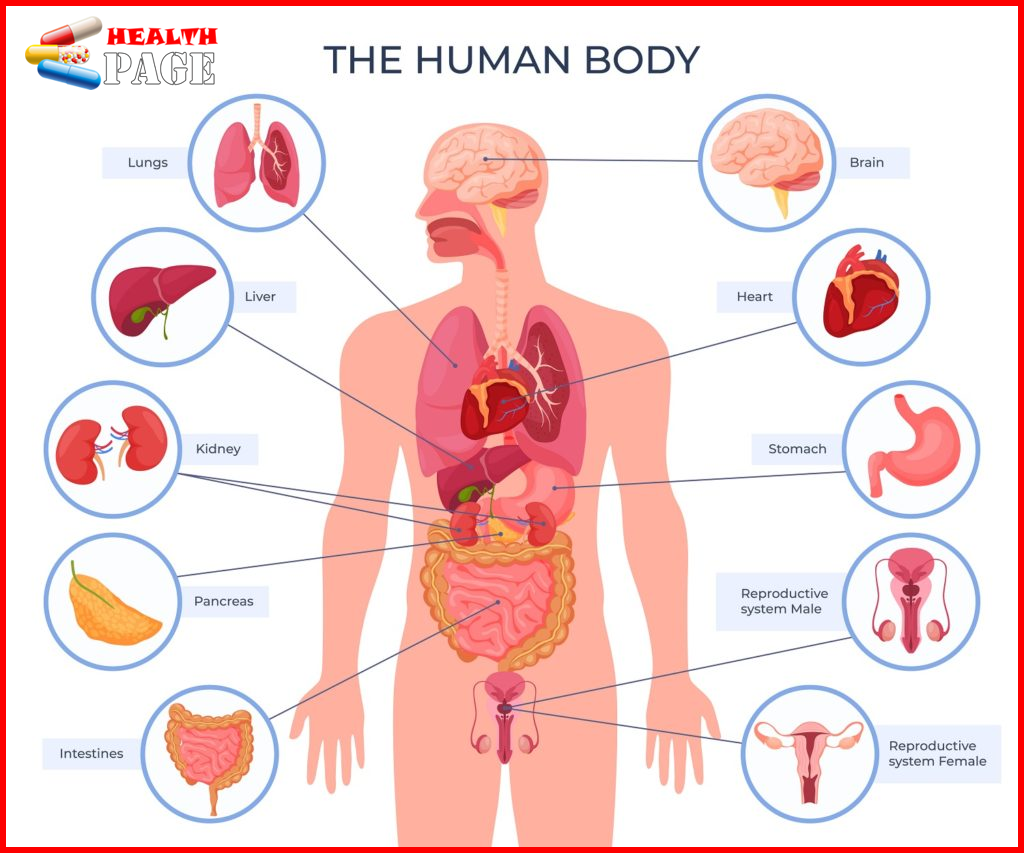
The complete info of the human body
The human body is a sophisticated, organic whole, with all parts working together and inseparable. No matter how small the error or disease is, it will cause a reaction throughout the body, as the saying goes, “a single hair moves the whole body.” Researchers often divide the human body into many systems based on the relative differences in the physiological functions of the various parts of the human body. According to the theory of anatomy, the human body can be divide into the following 10 systems.
Integumentary system
It is compose of skin, hair, fingernails/toenails, sweat glands and sebaceous glands, and is an organ covering the body surface.
Respiratory system
It consists of two parts: the respiratory tract and the lungs.
The respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi. Clinically, the nasal cavity, pharynx and larynx are call the upper respiratory tract, and the trachea and bronchi are call the lower respiratory tract. The walls of the respiratory tract are support by bones or cartilage to ensure smooth airflow.
The lungs are mainly compose of bronchial branches and the alveoli formed at their ends. Gases enter the alveoli and exchange gases with the blood in the capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
Oxygen inhale through the respiratory tract enters the capillaries through the alveoli, and is transport to various organs and tissues throughout the body through the blood circulation, supplying the organs with what they need for their oxidation processes; the metabolic products produced by various organs and tissues, such as CO2, are then transported to the lungs through the blood circulation, and then exhaled out of the body through the respiratory tract.
Digestive system
The digestive system consists of two major parts: the digestive tract and digestive glands. The digestive tract is a long muscular tube extending from the mouth to the anus, including the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, coelenteron, ileum) and large intestine (cecum, colon, rectum).
There are two types of digestive glands: small digestive glands and large digestive glands. Small digestive glands are scatter in the walls of various parts of the digestive tract, and large digestive glands include three pairs of salivary glands (parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands), liver and pancreas, all of which discharge secretions into the digestive tract through ducts.
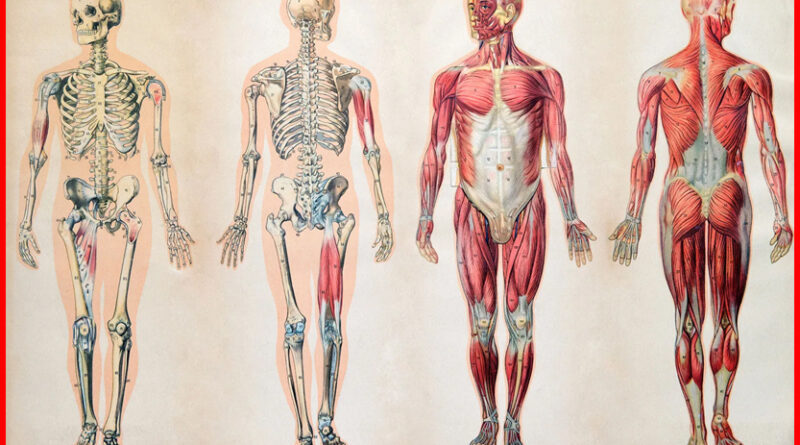
Musculoskeletal system
It is composed of bones, joints and skeletal muscles, forming a hard bone framework that gives the human body its basic shape.
Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and moves with joints as the fulcrum under the control of the nervous system. Skeletal muscle is striat muscle, which is control by nerves and contracts according to human will, also known as voluntary muscle. Adults have about 600 skeletal muscles.
Bones are mainly compose of bone tissue, with a certain shape and structure, covered with periosteum, containing bone marrow, and rich blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves. Adults have 206 bones, which can be divide into skull bones, trunk bones and limb bones.
Bones are connected by fibrous tissue, cartilage or bone, which is call a joint or bone connection. It can be divide into three categories: fibrous connection (fibrous joint), cartilage and bone connection (cartilaginous joint) and synovial joint. Synovial joint is often refer to as joint.
Nervous system
It is compose of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves that are connected to it and spread throughout the body. The brain and spinal cord are call the central nervous system.
Circulatory system
It know as the cardiovascular system, it is compose of the heart, blood vessels and blood, and is responsible for the transport of substances in the body.

Endocrine system
It is compose of endocrine glands and endocrine tissues in different parts and structures of the body, and it regulates the body’s metabolism, growth and development, and reproductive activities.
Lymphatic system
It is compose of lymphatic organs, lymphatic vessels at various levels and scattered lymphatic tissues, in which colorless and transparent lymph (fluid) flows. Its main function is to assist veins in transporting body fluids back to the blood circulation, convert fat and other macromolecules, and participate in the immune process. It is an important protective barrier for the human body.
Urinary system
Consists of kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
The waste (urea, uric acid, inorganic salts, etc.) and excess water produce by the body during metabolism need to be continuously send to the excretory organs through the blood circulation and excreted from the body. There are two channels for excretion: one is to form sweat through the sweat glands of the skin, and the other is to form urine through the kidneys and then excrete through the urinary tract. The amount and types of waste discharged by the kidneys are large. The kidneys are not only excretory organs, but also play an important role in maintaining the balance of electrolytes in the body.
Reproductive system
Consists of internal genitalia and external genitalia.
The male reproductive system is compose of gonads, testicles, ducts (epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct), accessory glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands), scrotum, and penis.
The female reproductive system consists of gonads/ovaries, ducts (fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina), and vulva (mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, vaginal vestibule, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, Bartholin’s glands). It has the function of reproduction.
The beauty of the human body
Leonardo da Vinci believed that the human body was beautiful if it met the following proportions. Today, this law of human proportions is still consider to be very valuable:
1. The head is 1/8 of the height;
2. Shoulder width is 1/4 of height;
3. The width of your arms when stretched out is equal to your body length;
4. The width of the armpits is equal to the width of the hips;
5. The breast is at the same level as the inferior angle of the shoulder blade;
6. The thickness of the front of the thigh is equal to the thickness of the face;
7. Reduce the kneeling height by 1/4.
Symmetry of the human body
In terms of external form, the human body’s structure and layout are symmetrical on both sides. For example, the back of the body is center on the spine, and the front of the body is center on the sternum. The breasts, shoulders and limbs are all symmetrical on both sides. The face is center on the bridge of the nose, and the eyebrows, eyes, cheekbones, ears, corners of the mouth and teeth are all symmetrical on both sides.
If this symmetry is destroy, it will not give people a sense of beauty, so symmetry restoration is one of the important principles of human beauty. However, if the parts of the human body are really absolutely symmetrical, it will lose its vivid beauty. It can be see that symmetry is also relative, not absolute.
The Golden Ratio
The discovery of the “golden section law” is the greatest discovery about the law of human beauty. The so-called golden section law refers to dividing a line or object of a certain length into two parts so that the ratio of one part to the whole is equal to the ratio of the other part to this part. This ratio is 0.618:1.
There are three golden section points in the human body:
The first is the Adam’s apple, which divides the distance from the throat to the top of the head and the distance from the throat to the navel at a ratio of 0.618:1.
The second is the elbow joint. The ratio from it to the shoulder joint to it to the tip of the middle finger is still 0.618:1.
Third, the ratio of the length of the middle finger to the length of the palm, and the ratio of the width of the palm to the length of the palm are both 0.618:1.
The ratio of the crown length to the crown width of the tooth is also very close to the golden ratio.
In terms of overall structure, human body parts are also divide according to the golden ratio. For example, the navel is the golden ratio point of the upper and lower parts of the body: the ratio of the body length above the navel to the body length below the navel is 0.618:1.
Therefore, some people have suggest that a body that meets the above ratios can be consider a handsome man or a beautiful woman with a standard body shape.
People have also discovered a more interesting phenomenon: the work and rest schedule that follows the golden ratio, that is, 15 hours of activity and 9 hours of sleep a day, is the most scientific and beneficial to human health. This is because 9 hours of sleep can optimize the activities of cells, tissues, organs and the coordination of various systems of the body, which is beneficial to the body’s metabolism and the recovery of physical strength and energy.
The Voice of the Human Body
When a person walks on an empty street or lies down to sleep late at night, it seems very quiet, but in fact his body is full of various sounds, and they are present everywhere and at all times. These sounds are often signs of the functional state of human organs, and therefore can be use as a basis for diagnosing diseases.
In 90% to 95% of healthy children, a “bing” sound can be hear at the upper chest using a stethoscope.
78% of healthy young people can hear a “crackling” sound similar to the flapping of butterfly wings on the right side of their neck.
People with hypertensive heart disease, coronary heart disease, and cardiomyopathy often have abnormal heartbeats that make sounds like wild horses galloping. In clinical medicine, this heart rhythm is call “galloping horse rhythm.”
People with hydrothorax or pyopneumothorax may hear a “dang, dang” sound like a small bell in their body. People with syphilitic heart disease may hear a “cooing” sound like a pigeon in their chest.
Patients with pneumonia that causes pleural effusion may hear a “bleating” sound in their bodies, similar to the bleating of sheep.
People with hyperthyroidism can hear a sound like the tide in their body.
The scientific community generally agrees that most of the sound information in the human body has not been fully understand and utilize, and there is still great potential for research in this area.
The best of the human body
The smallest radio station
Scientists have discovered that every cell in the human body is a miniature radio station that can emit radio waves with a frequency of 150 Hz, just lower than the listening frequency of a radio.
The longest pipe
The human body is covered with more than 100 billion tiny blood vessels. All of them were connected. They would be almost 100,000 kilometers long, more than twice around the earth.
The smallest “chemical plant”
Most of the metabolism in the human body is chemical changes. Under the control of hundreds of catalysts call “enzymes”, countless chemical reactions are carry out in sequence according to a series of strict and complex equations. Most of this is carry out in the smallest “chemical factory” – the liver, which weighs only 1.5 kilograms.
The most outstanding “water pump”
The human heart can work continuously for more than 100 years, pumping 6 to 8 tons of blood every day. The blood pumped in three and a half years is enough to float a 10,000-ton ship.
The most peculiar “steel”
The human body support entirely by bones. Bones are hollow, but have many texture structures that adapt to mechanical requirements. Each square meter of bone can withstand a weight of 1 ton.
The original engine
The lungs are like an engine that drives the body’s oxidative metabolism. When the lungs are at their maximum expansion in the chest cavity, they can hold 4.5 liters of air. It is calculated that the area of the lungs that absorb oxygen is 129,027 square centimeters, which is generally larger than the area of a small house. In addition, the internal surface area of the lungs is 50 times larger than the skin area.
Human data
American scientists have studied and compiled the following little-known human data:
1. A healthy adult loses about 45 hairs a day, and some people lose up to 60 hairs. However, there are about 120,000 hairs on the human scalp, so the loss of a few dozen hairs is insignificant. Most healthy people maintain a relatively balanced balance between hair loss and regrowth. According to the above hair loss data, a person can lose more than 1.5 million hairs in his lifetime, which is 12.3 times the total number of hairs.
2. Every 2 square inches of human skin has about 645 sweat glands, 77 feet of nerves, 1,000 nerve endings, 65 hair follicles, 75 sebaceous glands and 19 feet of capillaries. A healthy adult can shed 600,000 necrotic epithelial cells per hour. Based on this, he will lose 0.68 kilograms of skin every year. If he can live to 70 years old, he will lose 47.7 kilograms of skin in his lifetime. On average, there are 32 million bacteria per square inch of human body surface area, so there are 100 billion bacteria in the human body. Because there is a delicate relationship between the human body and bacteria, and between bacteria, and because human skin is a natural defense line, it does not show symptoms of disease under normal circumstances.
3. The human brain has a complex structure and sophisticated functions. Its nervous system is more than 1,400 times more complex than the world’s telephone network today. At the current level of technology, scientists can only draw a diagram of the working principle of a small part of the brain. The human brain has a total of 10 billion nerve cells, which can receive and process 86 million pieces of information every day.
The fastest speed at which the human brain transmits nerve impulses can reach 250 kilometers per hour. According to research, the human memory system has great potential and can accommodate 100 trillion pieces of information in a lifetime, which is a very large astronomical number. If a person is born and reads two numbers per second, 24 hours a day, he will not be able to count 5 billion by the age of 70. If he counts to 100 trillion, it will take 1.4 million years. Very complex chemical reactions occur in the human brain, an average of 100,000 times per second. If the energy of a human brain’s metabolism is directly convert, it can make a 20-watt light bulb glow.
4. Eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and body are our five sensory organs, which constantly receive various information from the outside world. However, only 1% of the information receive is processed by the brain, and the remaining 99% of the data is filter out as irrelevant information.
5. People can eat 40 tons of food and inhale about 5 million cubic meters of air through their mouths and throats in their lifetime. There are 9,000 taste buds on the human tongue, plus millions of nerve cells, which help us choose the food we like.
6. The energy of sound waves emitted by one person when speaking is very limited. But if people all over the world speak at the same time, the total energy of the sound waves they emit can exceed the electrical energy output of a large power station in one hour.
7. One minute after dark, the sensitivity of human eyes to light increases to 10 times; 20 minutes after dark, it increases to 6,000 times; 40 minutes after dark, the sensitivity of eyes to light reaches the limit, which is 25,000 times higher than before dark. Normal people’s eyes are very sharp. At night, people on the top of the mountain can see the light of a match 50 miles away.
8. After the reflected light from an object first enters the eye, the human brain takes only 0.05 seconds to recognize the object.
9. The olfactory receptor patches of a healthy adult are only 3/4 square inch in size, while those of a hound are at least 10 square inches, those of a shark are 24 square inches, and those of a mouse are almost as large as the skin area of its entire body.
10. The human heart beats day and night, and the energy it consumes every day is equivalent to the energy required to lift an object weighing about 2,000 pounds to a height of 41 feet. When a person is 50 years old, the total amount of work done by his heart is equivalent to lifting 18,000 tons to a height of 142 miles.
11. An adult has 5 to 6 liters of blood in their body. It contains 25 trillion red blood cells (transporting oxygen) and 25 billion white blood cells (resisting disease). The average life span of red blood cells in human blood is 4 months, and some white blood cells only live for 12 hours. Based on the circulation speed in the blood, a red blood cell can travel more than 1,600 kilometers in total.
12. When a person lies in bed, he or she only needs to inhale about 8.8 liters of oxygen per minute; when sitting quietly, the oxygen consumption is doubled, consuming 17.6 liters; when walking, the oxygen consumption is 26.4 liters per minute, which is three times that of lying still; when running, it is as high as 55 liters per minute. The average person breathes about 500 million times in total in his or her lifetime.
13. Lack of sleep is more likely to kill people than hunger. People will die if they don’t sleep for 10 days, but hunger may last for several weeks.
14. A person weighing 60 kg has 75 tons of water, 17.5 tons of sugar, 2.5 tons of protein, and 1.3 tons of fat in and out of his body during his 60 years of life, totaling 96.3 tons. These things can fill 24 4-ton trucks, which is equivalent to 1,600 times his own body weight.
15. The human body has about 100 trillion cells in total, and there are about 100 trillion cell divisions in a lifetime. If a person can live to be 100 years old, then on average, 300 billion cells will divide every day, and on average, 3 million cells will divide every second.
16. The human body also contains a number of other substances: fat enough to make 7 bars of soap; lime enough to paint a small room; carbon content equivalent to a 13 kg bag of coke; phosphorus content enough to make 2,200 matches; and iron as much as a 2.5 cm long nail. In addition, there is about 1 spoonful of sulfur and 1 ounce of other metals except iron.
17. A newborn baby has 305 bones, which later become 206 (the number varies slightly due to a few exceptions), controlled by 650 muscles and more than 100 joints. The tendons that fix the muscles and bones are extremely tough and can withstand a pressure of 8 tons per square inch.
Human body regeneration
Some lower mollusks, such as leeches and starfish, have strong regenerative abilities. Even if you crush them completely, each fragment can still grow into a new individual. As a higher animal, humans do not have this ability, but they are not completely without regenerative ability – some organs in the human body have the ability to regenerate.
The regenerative ability of human tissues or organs can be divided into three situations: one is a very strong regenerative ability, which can regenerate continuously under normal physiological conditions, such as skin, small blood vessels, liver, etc.; one is a limited regenerative ability under normal physiological conditions, such as muscles, cartilage, nerve tissue, etc.; and the other is no regenerative ability or very weak regenerative ability, such as central nervous tissue.
The tissues or organs with the strongest regenerative ability are often those that are easily damaged or that need to be frequently renewed due to physiological needs, such as skin, red blood cells, mucous membranes, fibrous tissue, small blood vessels, bone marrow, bone tissue, liver cells, etc. Skin is the most easily injured tissue in the human body, so skin regeneration is the most common. The regenerative ability of red blood cells is amazing.
Even if you donate several thousand milliliters of blood, you can quickly regenerate and replenish it, and it will have little impact on your health. The regenerative ability of the liver is also very strong. As long as 20% of the liver tissue functions normally, the liver may be able to restore its full function. People who have had most of their liver removed can regenerate to their original size through the hepatocytes in the healthy liver lobules.
Some organs or tissues can only regenerate within a limited range, and this is related to the degree of injury, nutrition, etc. For example, bone tissue can regenerate as long as there is periosteum left, but it cannot generate new limbs.
Highly differentiated and functionally complex tissues or organs such as heart and ganglion cells are difficult to regenerate.
Compensation – replacement and compensation – is an important function of human organs similar to regeneration. The function of an organ or tissue removed due to disease or other reasons can be replaced by the remaining or other organs or tissues. For example, for paired organs such as lungs, kidneys, and testicles, after one is removed, the function of the other will be greatly enhanced to compensate.
Human body clock
Just like a clock that cycles 24 hours a day, most organisms also have a functional rhythm, so it is called a “biological clock” rhythm. With a 24-hour cycle, the various functions of the human body show the following changes:
At 1 a.m., most people have been asleep for several hours. They are in a light sleep stage from which they can be easily awakened, and are particularly sensitive to illness.
2:00 During this time, the liver is very active, stepping up the production of substances needed by the human body, while stepping up the removal of substances that are toxic to the human body from the liver and blood, as if it is doing a “house cleaning” in the human body. Most organs work more slowly.
At 3 o’clock, muscles are completely relaxed, blood pressure drops, breathing and heart rate decrease, and the whole body enters a resting state.
At 4 o’clock, the blood supply to the brain reaches the lowest point of the day, and the blood pressure drops further. Although the working rhythm of the organs of the whole body is relatively slow, the hearing is sensitive and wakes up at the slightest noise. This is the time when patients with various serious diseases are prone to death.
After going through light sleep, dreaming, and deep sleep at 5:00, people’s energy is basically restored. If you get up at this time, you will feel full of energy. The kidneys are almost not working.
At 6 o’clock, the heart rate speeds up and the blood pressure starts to rise. People often don’t want to get up and have a feeling of insecurity.
7 o’clock, the human body’s immune function reaches its peak state, and at this time the body has a stronger resistance to invasion by bacteria or viruses.
8 o’clock, all toxic substances in the liver are eliminated, so it is not advisable to drink alcohol.
9 o’clock, the heart enters full load state, responsiveness and activity increase, and pain decreases.
10 o’clock, people are full of energy, which is the best time to work, study and exercise.
11 o’clock, the heart is still working very hard and the human body is less likely to feel tired.
12 o’clock, all organs and systems are active, and the whole body is in full mobilization. It is best to postpone lunch at this time.
13:00 is the best time for working in the first half of the day. It is easy to feel tired, so it is best to take a lunch break. Some glycogen enters the blood and the liver gradually enters a resting state.
The human brain becomes slow to react at 2 p.m., which is the second lowest activity point in the 24 hours of the day.
At 15:00, the situation began to improve and the ability to work gradually recovered.
Sensitivity, especially to smell and taste.
Blood sugar increases at 16:00, but will drop back down quickly, so it generally does not cause disease.
17:00 is the best time for athletes to strengthen their training as work efficiency is higher.
The pain will subside again at 18:00 and you can increase your activity level appropriately.
At 19:00, blood pressure rises, emotions become unstable, and temper tantrums are easy to occur.
20:00: The drivers are more responsive and their weight reaches the highest value of the day. At this time, the drivers are less likely to have car accidents.
At 21:00, people react quickly and have enhanced memory, so they can remember a lot of things that they didn’t remember during the day. It is the most suitable time for memorizing and learning.
At 22:00, the blood cell content in the blood increases to 12,000 per cubic centimeter; the body temperature drops.
At 23:00, energy decreases, fatigue gradually increases, and the body’s functions need to be restored, so the human body should enter a resting time.
24 hours is the last moment of the day, when most people fall into a sweet dream; the activities of various organs and systems of the human body weaken.

Pingback: Prostavive Colibrim: The Natural Solution for Prostate Health