Eat more lotus roots now! There are more than one reason
lotus roots are very popular. Some have a sweet and crispy taste, some have a soft and sticky taste, and some are somewhere in between. Fried lotus root boxes, lotus root stir-fried lotus root, cold lotus root slices, glutinous rice lotus root, etc. are all commonly eat. Are you drooling?
Now is the season for eating lotus roots, so you certainly can’t miss it. Take advantage of the opportunity to eat more lotus roots.
How nutritious is lotus root?
Lotus root has a history of more than 3,000 years of cultivation. It is the rhizome of lotus in the soil and is a common aquatic vegetable. It is called the “Eight Water Immortals” together with aquatic plants such as wild rice stem, water chestnut, Euryale ferox, water celery, water shield, arrowhead and water chestnut. Lotus root mainly contains carbohydrates, dietary fiber, protein, vitamin C and mineral potassium.

carbohydrate
The carbohydrate content of lotus root is 11.5g/100g. Although it is lower than that of potatoes and sweet potatoes, it is higher than most vegetables we eat. The starch content of different varieties of lotus root varies. Some lotus roots, such as the lotus root, have a starch content of only 1.3g/100g, while the starch content of the lotus root from Honghe, Yunnan is 13.7g/100g.
Therefore, some lotus roots with a soft and sticky texture are not suitable for eating as vegetables. If you like to eat lotus roots but want to take your weight into consideration, it is recommend to eat less rice.
Dietary fiber
According to data from the Chinese Food Composition Table, the insoluble dietary fiber content of lotus root is 2.2g/100g, which is twice that of potatoes. The dietary fiber content of different lotus root varieties also varies. Studies have shown that the total dietary fiber content of lotus root from Heze, Shandong Province is the highest, at about 7g/100g.
Mineral Potassium
The potassium content of lotus root is 293 mg/100 g, and the potassium content of Yunnan Red River lotus root can reach 407 mg/100 g, which is 1.6 times that of banana.
Vitamin C
Most lotus roots have a good vitamin C content. A study compared the nutritional components of lotus roots from 10 production areas and found that the vitamin C content was between 50% and 70%. The vitamin C content of lotus roots, at around 68 mg/100 g. This content is higher than that of oranges and kiwis.
However, cooking will cause some loss of vitamin C. The retention rates under boiling, steaming, frying, and microwave conditions are 61.35%, 93.91%, 76.56%, and 85.87%, respectively. From the data, except for boiling, other cooking methods do not cause much loss, which is still very helpful for our daily vitamin C supplementation.
protein
Lotus root has the highest protein content among vegetables. The protein content of lotus root from Jingzhou, Hubei Province is as high as 3.8g/100g, which is higher than most vegetables. However, lotus root lacks methionine and isoleucine in its amino acid nutrition evaluation. Therefore, when eating lotus root, it is best to eat it with seaweed and beans to improve the absorption and utilization rate of protein.
In addition, lotus root also contains antioxidants and calcium, zinc, iron and selenium.
As for the lotus root starch that is commonly eat, it mainly refers to pure starch extract from lotus roots, which contains a certain amount of resistant starch. When mixed with warm water, it will form a gel state, which has a strong sense of fullness and a GI value of only 33. It is a low-GI food and can be eat even by diabetics.
What are the health benefits of eating lotus root regularly?
Lotus root is so nutritious, friends who love to eat lotus root can make arrangements! A lotus root the size of a palm is about 200 grams, and a lotus root the size of a fist is about 100 grams! What are the benefits of eating more lotus root?


Helps lose weight and prevents constipation
Lotus root has very low calories, only 47kcal/100g, which is lower than sweet potatoes, potatoes, and yam. It is also rich in dietary fiber. Eating 100 grams of Shandong Heze lotus root can meet 28% of the minimum dietary fiber requirement of the general population. It not only has a strong sense of fullness and helps control appetite, but also promotes gastrointestinal motility and prevents constipation. Therefore, eating lotus root correctly can really make you “slim”!
Stabilize blood pressure
If you can eat 100 grams of Yunnan Red River lotus root every day, you can meet 20% of the general population’s daily potassium needs, which is very helpful for controlling blood pressure.
Enhance immunity
The rich vitamin C in lotus root can promote the production of antibodies, enhance body resistance, and also help maintain skin health. Eating 100 grams of lotus root can meet nearly 50% of the general population’s vitamin C requirement.
Antioxidant
Lotus roots are also rich in antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, which help to remove excess free radicals from the body and have anti-inflammatory effects.
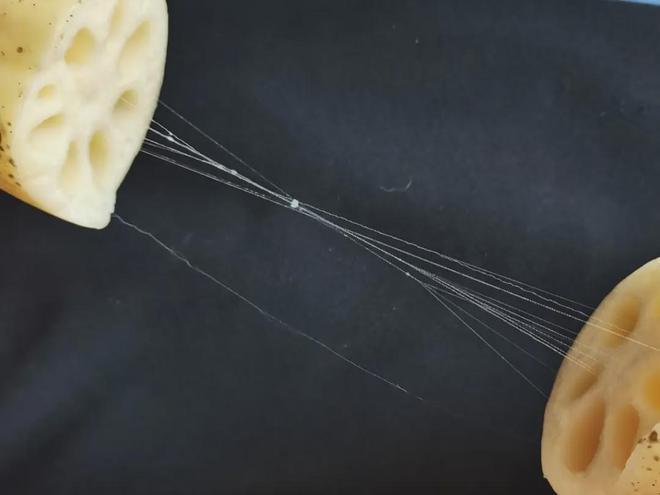
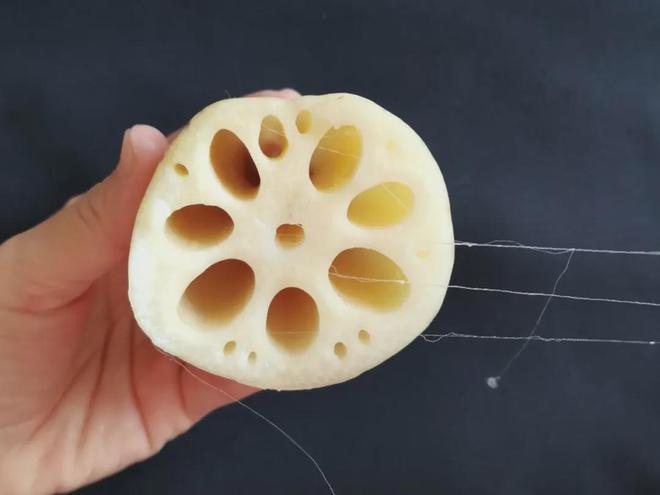
After the lotus root is broken, there will be a phenomenon of broken threads connected. The threading of lotus root is different from that of yam. The threading of yam is caused by mucus, but the threading of lotus root is not mucus, but the duct wall (annular duct wall) of the spiral duct in the internal transport tissue of the lotus root. When the lotus root is cut, the duct wall will be stretch like a spring.
If you look closely, you will find that this “lotus root drawing” is thread-like, and to the naked eye it looks more like a “wavy line” rather than a “straight line”.
Why does lotus root change color?
Friends who often eat lotus root will have the experience that lotus root is a “color change king”. It will change black after being cut and get red when boil in soup. Why is this?
The lotus root get change black after being cut because it contains phenolic substances. After being cut, it will undergo enzymatic browning when it comes into contact with enzymes and oxygen. The quinones produced in this process will polymerize into colored substances, causing the surface of the cut lotus root to gradually turn brown. The longer it is left, the dark the color will be, and eventually it will change black.
If you cannot cook it immediately after cutting, soak it in clean water as soon as possible. Isolating the oxygen will prevent the oxidation reaction and maintain the color of the lotus root. But don’t leave it for too long, or it will deteriorate.
It is normal for the soup to turn red when cooked. This is because lotus root contains proanthocyanidins, which are also a type of phenolic substance. After being treat at high temperatures, they will be oxidize into anthocyanins and then turn red.

How to store lotus root?
If the purchase lotus root is not store properly, it will easily turn brown, lose its hardness, and have a bad taste. Storage temperature is a key factor affecting the quality of food. Low-temperature storage can effectively regulate the physiological activities of fruits and vegetables, reduce the speed of various physiological and biochemical reactions, and delay the decline of fruit and vegetable quality.
If the purchase lotus root only needs to be store for a short period of time, it can be soak in cold water and refrigerated. If it needs to be store for a long time, it is recommend to store it at -1°C within 10 weeks of storage. This can better maintain the appearance quality and higher flesh hardness of the lotus root, and can also delay the browning of the lotus root.


Pingback: Many people have never eaten cherry radish.