Let’s know about influenza a vs b
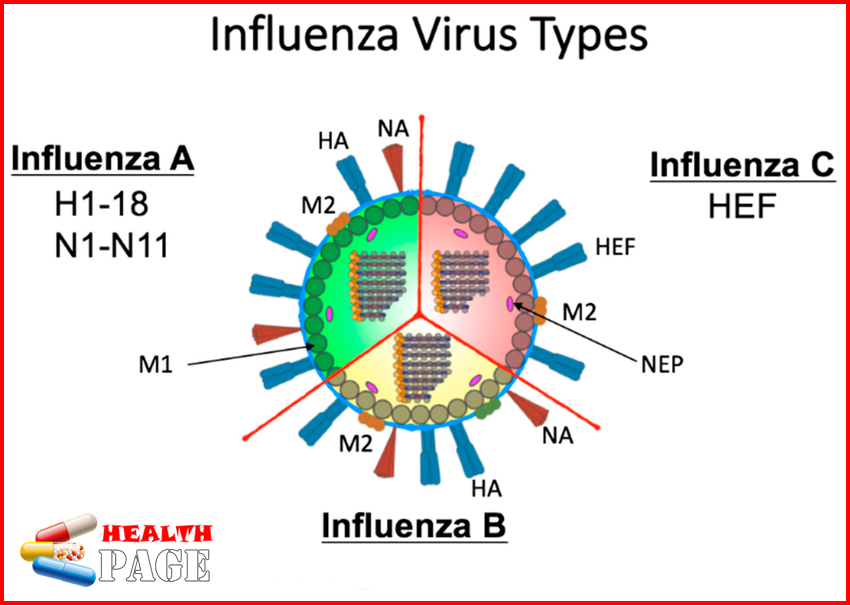
Inthis article we are going to tell about influenza a vs b. Influenza refers to the disease cause by influenza virus, which is divide into three types: A, B and C according to the difference in nucleoprotein and matrix protein. Influenza virus is divide into A, B or C according to the complement binding antibodies of nucleoprotein and matrix protein. Hemagglutinin (H) is a glycoprotein on the surface of influenza virus, which allows the virus to bind to cellular sialic acid and fuse with the host cell membrane. Neuraminidase (NA) is another surface glycoprotein that can remove sialic acid to prevent the virus from being released by the infected host.
Influenza A virus is a common influenza virus. Influenza A virus is most likely to mutate, and avian influenza (abbreviated as human-avian influenza) is an acute respiratory infectious disease cause by some strains of certain subtypes of avian influenza A virus. After the virus gene mutates , it can infect humans. The symptoms after infection are mainly high fever, cough, runny nose, myalgia, etc. Most of them are accompanied by severe pneumonia. In severe cases, multiple organ failure such as heart and kidney leads to death, and the mortality rate is very high.
Influenza B virus is an influenza virus cause by type B virus. It is characterize by an acute onset, chills, and fever. The body temperature reaches a peak of 39-40°C or even higher within a few hours to 24 hours.
As a supplier of biological raw materials, KMD Bioscience has develop antigens and antibodies covering the fields of infectious diseases, fertility, cardiac markers, tumor markers , inflammation and serum proteins, which are widely use in various technical platforms such as immunochromatography , ELISA, chemiluminescence, PCR, etc. After years of innovation and development, the company has built multiple technical platforms, including colloidal gold/latex immunochromatography technology platform, fluorescent immunoassay technology platform, chemiluminescence technology platform and molecular diagnostic technology platform. KMD Bioscience can provide high-quality and sensitive diagnostic raw materials: influenza A (B) virus protein and mouse monoclonal antibody
Molecular structure and subtypes of FluA and FluB:
Influenza A viruses are divide into many subtypes base on their H and N antigens. H can be divide into 18 subtypes (H1 to H18) and N has 11 subtypes (N1 to N11 [4]). Among them, only H1N1, H2N2, and H3N2 mainly infect humans. H1N1 and H3N2 are the main subtypes that cause seasonal influenza. The natural hosts of many other subtypes are various poultry and animals.
Influenza A virus is most prone to mutation, and influenza pandemics are cause by the emergence of new subtypes of influenza A virus or the reappearance of old subtypes. The surface antigens of influenza A virus often undergo small mutations, which are call “antigenic drift”. Figuratively speaking, “drift” means that the virus disguises itself through small changes to avoid recognition by the human immune system. The result of influenza A virus “drift “ is that the strains that cause influenza may be different every year, and people need to be re-vaccinate with influenza vaccines every year for prevention.
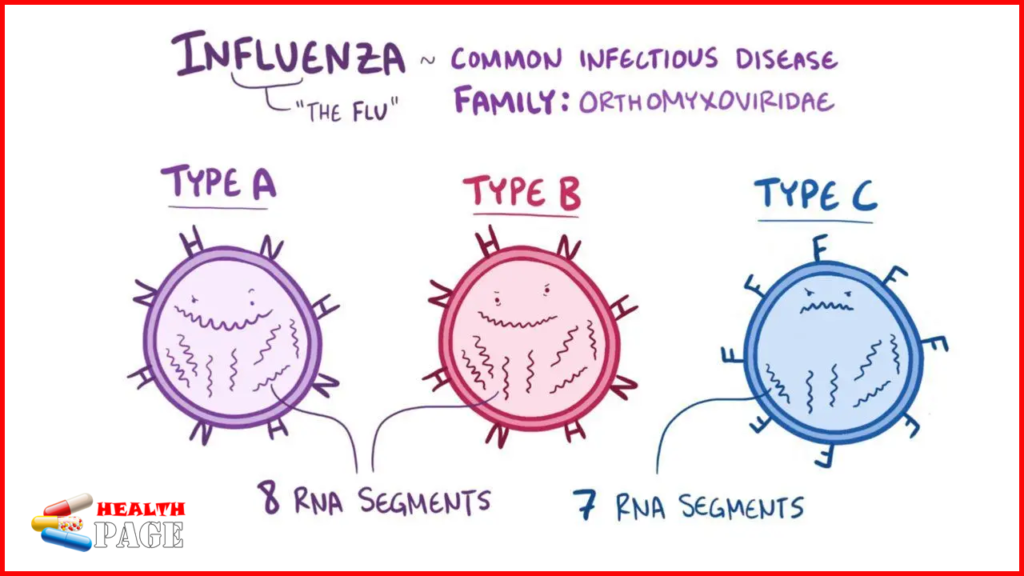
Biological characteristics of FluA and FluB
Influenza viruses usually invade the human body by combining a certain part of the viral protein with a specific protein in the human body. Because through such combination, the influenza virus can suppress the human body’s own natural defense system against viral infection, paving the way for the virus to effectively replicate in the human body.
Antigenic shift only occurs in type A viruses. It is cause by genetic reassortment between viruses when two viruses from humans and animals infect the same cell. The resulting viral hemagglutinin and neuraminidase undergo a completely new combination, making the population immune. Antigenic shift is the cause of the global influenza pandemic. Type A influenza viruses undergo a major mutation approximately every ten years. Since 1933, type A viruses have undergone four antigenic shifts: H0N1 (original type A, A0) from 1933 to 1946, H1N1 (subtype A, A1) from 1946 to 1957, H2N2 (Asian type A, A2) from 1957 to 1968, and H3N2 (Hong Kong type, A3) after 1968.
Generally, there is a clear alternation between the new and old subtypes. After the new subtype appears and spreads to a region, the old subtype can no longer be isolate. There are also large and small mutations between type B influenza viruses, but they are not divide into subtype shifts. No antigenic variation has been found in influenza C virus .
Products and advantages:
KMD Bioscience, with its rich R&D experience and advanced technology platform, has launched high-quality “all-round” technical services, mainly including antibody discovery ( hybridoma monoclonal antibody technology, Beacon single cell sorting technology, phage display technology ), protein expression (prokaryotic protein expression, yeast cell protein expression, insect cell protein expression, mammalian cell protein expression). The production of our antigens is rigorously designed and strictly evaluated for performance, and has excellent stability and specificity. Moreover, our antigen raw materials can be use in the research and development of standards , calibrators, quality control products and as immunogens .

Pingback: Azithromycin usage, all explained in one article
Pingback: Latest updates on breast cancer screening icd 10