How i knew i had bladder cancer?
Bladder cancer is a malignant disease, the cause of which can be due to smoking, exposure to chemicals, polluted environment, etc. Ultrasound can detect tumors but cannot accurately diagnose and assess the stage of bladder cancer. How i knew i had bladder cancer? Therefore, patients need to do some additional paraclinical measures such as cystoscopy, CT scan, urine test, etc.
1. What is bladder cancer?
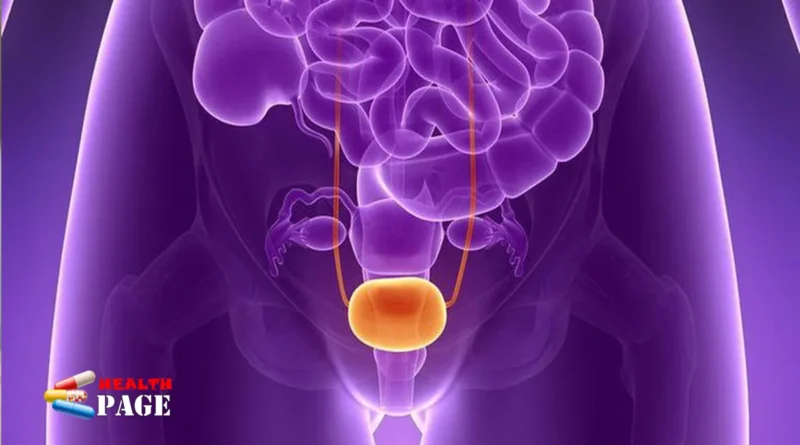
Bladder cancerare cells in the bladder that mutate, grow abnormally and uncontrollably, and form a tumor in the bladder.
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the lower abdomen that stores urine excreted by the kidneys. The inside of the bladder is a mucosal layer made up of transitional cells and squamous cells.
About 90% of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas, and 8% of bladder cancers are squamous cell carcinomas.
2. Causes of bladder cancer
The cause of bladder cancer is currently unknown. However, some factors that have been linked to bladder cancer include:
- Smoking
- Radiation exposure
- Parasitic infection
- Chemical exposure
- Polluted environment
- Family history of bladder cancer
- Occupations that regularly expose you to toxic substances such as: rubber, chemicals, hairdressers, printers, weavers, etc.

3. Symptoms of bladder cancer
Symptoms of bladder cancer are often difficult to detect. Some basic symptoms in the early stages of bladder cancer include:
- Tired, lost weight
- Blood in urinecan be intermittent, gross hematuria, total hematuria.
- Painful urination
- Urinary frequency, difficulty urinating, urinary incontinence
- Dark urine
- Some symptoms urinary tract infection, urinary obstruction.
4. Can ultrasound detect bladder cancer?
Bladder ultrasound is the first diagnostic imaging method indicated when patients have problems with urination disorders.
Ultrasound can detect stones,congenital defectand detect tumors, assess the extent of invasion of the bladder wall or ureter causing hydronephrosis or not. However, ultrasound cannot diagnose and assess the stage of bladder cancer, cannot assess the depth of invasion, spread outside the bladder or lymph node status.
Therefore, the doctor may prescribe some other paraclinical measures to help diagnose bladder cancer such as:
- CT scan or MRI: CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis allows assessment of tumor extent, metastasis to pelvic or retroperitoneal lymph nodes, visceral, pulmonary, bone metastasis, and upper urinary tract obstruction.
- UIV shooting: Mainly used to assess renal function when there is suspicion of renal damage due to tumor invasion, ureteral compression or chronic urinary tract infection.
- Bone scan: Bone scan is indicated when there is invasive cancer or locally advanced tumor and the patient has bone pain or increased alkaline phosphatase levels.

- PET-CT scan: PET-CT scan has little value in assessing local lesions but plays a major role in assessing metastasis.
- Urine test: Look for red blood cells, cancer cells in the urine, or other signs of bladder cancer.
- Contrast venography: Doctors willX-rayto detect abnormalities in the bladder by injecting contrast material into the vein. These substances will be excreted by the kidneys and concentrated in the bladder.
- Cystoscopy: During this procedure, patients will be anesthetized. The doctor may take a small sample of tissue through the cystoscope and perform a pathological anatomy, biopsy to confirm whether there is cancer or not. In a few cases, the doctor may remove the entire cancerous area during the biopsy, in which case the biopsy is both diagnostic and therapeutic.

5. Bladder cancer treatment
If detected early, bladder cancer can be easily cured. Treatments for bladder cancer include:
5.1 Surgery
Is a common method in treating bladder cancer. Depending on the stage and grade of the tumor, the doctor performs the appropriate type of surgery such as: transurethral resection of bladder tumor, partial cystectomy, total cystectomy, resection of nearby organs containing cancer cells.
5.2 Radiation
This method can be performed before surgery to reduce the size of tumors. Or radiation is performed after surgery to destroy remaining cancer cells. For bladder cancer patients who cannot undergo surgery, radiation will be performed in two ways: internal radiation and external radiation.
5.3 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of one or more drugs in combination to kill cancer cells.
To prevent bladder cancer, it is necessary to have a healthy lifestyle such as avoiding exposure to chemicals and polluted water sources, not smoking, and having a reasonable diet. Moreover, bladder cancer can be cured if detected early, so it is necessary to have regular check-ups every 6 months for timely detection.
In summary, bladder cancer is a malignant disease caused by cells in the bladder that mutate, grow abnormally and uncontrollably, and form tumors in the bladder. Bladder ultrasound is a diagnostic method that can detect tumors. However, ultrasound cannot diagnose and evaluate the stage of bladder cancer, the spread outside the bladder or the status of the lymph nodes, so some other paraclinical tests are still needed. Bladder cancer can be cured if detected early.

Pingback: What is cancer? The most complete and detailed information