Top 7 Critical Facts About Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 You Must Know
Proper coding of abdominal aortic aneurysm ICD 10 helps save lives through accurate medical records.
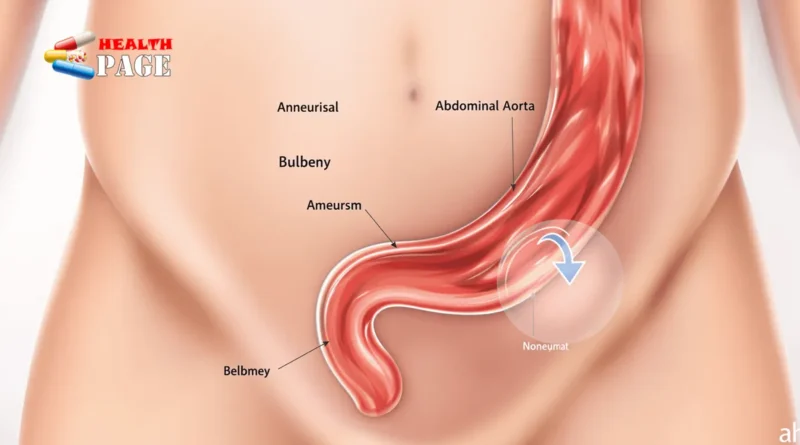
An abdominal aortic aneurysm happens when your main blood vessel gets bigger in your belly area. This serious condition needs careful watching and proper medical coding to track patient care.
Medical coding might sound boring, but it’s super important for:
- Getting the right treatment to patients
- Making sure insurance pays correctly
- Keeping track of how many people have this condition
- Helping doctors share information clearly
Think of ICD-10 codes like a special language doctors use to talk about AAA. These codes tell the whole story:
- Where exactly the problem is
- How serious it is
- What kind of treatment you need
The critical facts about AAA coding can mean the difference between life and death. Wrong codes can lead to:
“Delayed treatments, denied insurance claims, or mixed-up medical records – things nobody wants when dealing with a serious health condition.”
This guide walks you through the seven most important things you need to know about AAA ICD-10 coding. Let’s make sure you understand each piece of this vital medical puzzle.
1. ICD-10 Code for AAA Without Rupture (I71.40)
The ICD-10 code I71.40 marks a key classification for abdominal aortic aneurysm without rupture. This code helps doctors track cases where the aorta wall bulges but hasn’t broken.
Medical coders use I71.40 to show these specific details:
- The aneurysm sits in the abdominal part of the aorta
- No rupture has happened
- The exact location remains unspecified
The I71.40 code becomes active on October 1, 2024. This update brings better tracking of AAA cases in medical records.
Proper use of I71.40 matters for several reasons:
- Insurance Claims: Wrong codes can lead to denied claims
- Patient Records: Clear coding helps track treatment history
- Research: Good data helps study AAA patterns
- Hospital Planning: Accurate counts guide resource allocation
Healthcare providers must note these details for I71.40:
💡 The code needs proof of:
- AAA presence through imaging
- No rupture signs
- Clear documentation in patient files
Billing staff check these points before using I71.40:
- Patient symptoms match the code
- Doctor’s notes support the diagnosis
- No other AAA codes fit better
This specific code helps create a standard way to track and bill AAA cases across all healthcare settings.
2. Code I71.4 History and ICD-10 Conversion Impact
The ICD-10 code I71.4 has gone through significant changes since its introduction in 2016. Let’s look at its evolution:
2016-2023 Timeline:
- I71.4 served as a direct code for AAA without rupture
- Healthcare providers used this single code for billing
- Medical records relied on this code for classification
2024 Changes:
- I71.4 transforms into a parent code
- New sub-codes emerge for specific conditions
- Greater detail in diagnosis documentation becomes mandatory
The parent code status brings new sub-classifications:
- I71.40 – Unspecified AAA without rupture
- I71.41 – Suprarenal AAA without rupture
- I71.42 – Pararenal AAA without rupture
- I71.43 – Infrarenal AAA without rupture
These changes affect medical coding practices in several ways:
- Documentation RequirementsDoctors must specify aneurysm location
- Size measurements become crucial
- Regular updates to patient records needed
- Billing ProcessMore specific codes for insurance claims
- Better tracking of treatment outcomes
- Improved data accuracy for research
- Staff TrainingMedical coders need updated knowledge
- Healthcare providers require new documentation habits
- Administrative staff must adapt to new systems
The 2024-2025 changes create a more detailed coding system. This new structure helps track patient care with greater precision.
3. Aortic Aneurysm Codes in Circulatory System Diseases Category
The ICD-10 system places abdominal aortic aneurysm codes within the I00-I99 range. This range covers diseases of the circulatory system.
AAA codes belong to the I71 series, which includes:
- I71.00 – Dissection of unspecified site of aorta
- I71.02 – Dissection of abdominal aorta
- I71.3 – Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm
- I71.4 – Abdominal aortic aneurysm without rupture
The specific location of the aneurysm determines the exact code selection:
Suprarenal: I71.41 Juxtarenal: I71.42 Infrarenal: I71.43 Unspecified: I71.40
Medical coders must understand these subdivisions for accurate coding:
- Thoracic aorta codes: I71.1, I71.2
- Thoracoabdominal codes: I71.5, I71.6
- Abdominal aorta codes: I71.3, I71.4
The ICD-10 system includes additional codes for:
- Aortic ectasia (I71.9)
- Aortic dilatation (I71.9)
- Multiple aneurysms (I71.8)
These codes help track patient outcomes and guide treatment decisions. The detailed classification system supports precise medical documentation and proper insurance claims processing.
4. Importance of Specific Sub-Codes for Detailed Coding Practice (e.g., Infrarenal AAA – I71.43)
Specific sub-codes help medical professionals pinpoint exact AAA locations for better patient care. Let’s look at the key benefits:
Accurate Medical Records
- Helps track disease patterns
- Supports research studies
- Creates detailed patient histories
- Enables precise treatment planning
The infrarenal AAA code (I71.43) shows how specific sub-codes work in practice. This code tells us:
- The aneurysm sits below the kidneys
- No rupture has occurred
- The condition needs monitoring
Location-Based Sub-Codes Include:
- I71.41 – Suprarenal
- I71.42 – Pararenal
- I71.43 – Infrarenal
- I71.44 – Juxtarenal
These specific sub-codes create a clear picture of each patient’s condition. A doctor reading I71.43 knows exactly where to look during imaging studies.
Benefits of Detailed Coding:
- Fast treatment decisions
- Better insurance claims
- Clear communication between doctors
- Improved patient outcomes
Proper sub-code use helps hospitals track AAA cases by location. This data shapes treatment protocols and resource allocation.
Medical coders must check the operative notes for exact aneurysm location. Wrong location codes can lead to denied claims or treatment delays.
Detailed sub-codes also help identify high-risk cases. Doctors use this info to plan follow-up care and prevent complications.
5. Endovascular Repair Procedures for AAA: Distinct Coding Considerations
Endovascular repair procedures create unique coding paths that need careful attention. Medical coders must understand specific repair types to assign the right codes.
Standard Endovascular Repairs
- 34701: Basic endovascular repair
- 34702: Repairs with tube prosthesis
- 34703: Modular bifurcated prosthesis
- 34704: Unibody bifurcated prosthesis
Fenestrated Graft Considerations
Fenestrated grafts need special codes due to their complex nature:
- 34705: Initial placement
- 34706: Follow-up procedures
- 34707: Artery involvement
- 34708: Multiple vessel repairs
Key Documentation Requirements:
- Graft type used
- Access method
- Vessel measurements
- Repair locations
- Imaging guidance
Additional Procedure Codes
Repairs might need extra codes for:
- Imaging guidance
- Device placement
- Vessel access
- Closure methods
- Complications
Reimbursement Tips
Proper coding affects payment rates:
- Check payer guidelines
- Document medical necessity
- Include size measurements
- Report all components
- Note any complications
Modifier Usage
- -RT: Right side
- -LT: Left side
- -50: Bilateral
- -22: Increased procedural services
These codes help track patient outcomes and support quality reporting measures. Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement for these complex procedures.
6. Essential Clinical Documentation Needs for Accurate ICD-10 Coding: Rupture Status, Aneurysm Location, Size, and Type Considerations
Proper clinical documentation is essential for accurate ICD-10 coding in cases of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Medical records must contain specific information to ensure the correct code is chosen.
Key Documentation Elements:
- Rupture status (whether it is ruptured or unruptured)
- Exact location of the aneurysm (infrarenal, juxtarenal, suprarenal)
- Size of the aneurysm in centimeters
- Type of aneurysm (fusiform, saccular, dissecting)
- Any complications present
- Methods of treatment used
Size Documentation Requirements:
- Small: Less than 4 cm
- Medium: 4-5.2 cm
- Large: Greater than 5.2 cm
The rupture status affects immediate treatment choices. If the AAA is ruptured, emergency intervention is necessary and specific ICD-10 codes such as I71.3 will be used.
Location Documentation Guidelines:
Infrarenal → I71.43 Juxtarenal → I71.42 Suprarenal → I71.41
Medical providers should also take note of any related conditions:
- Arterial embolism
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Hypertension
- Atherosclerosis
Clear documentation is crucial in preventing coding mistakes. Every detail in the medical record supports the assignment of a specific code.
Required Elements in Operative Notes:
- Pre-operative diagnosis
- Post-operative diagnosis
- Detailed description of the procedure
- Complications encountered
- Estimated blood loss during the procedure
- Specifications of any implants used
These documentation elements are necessary for proper reimbursement and also support quality tracking measures for AAA treatment outcomes.
7. Importance of Accurate ICD-10 Codes in Reimbursement Claims and Quality Indicators
Accurate ICD-10 codes are essential for successful reimbursement claims for AAA treatments.
Healthcare providers must submit precise codes to receive proper payment for their services:
- Incorrect codes result in claim denials
- Correct codes expedite payment processing
- Specific codes validate medical necessity
- Proper coding supports appeal processes
The financial impact of coding accuracy goes beyond basic reimbursement:
“Each AAA procedure can cost between $12,000 to $35,000, making accurate coding crucial for hospital revenue.”
Role of ICD-10 Coding in Quality Metrics Tracking
Proper ICD-10 coding is vital for tracking quality metrics such as:
- Monitoring patient outcomes
- Tracking surgical success rates
- Comparing hospital performance
- Identifying treatment patterns
- Measuring readmission rates
Significance of Hospital Discharge Data Powered by ICD-10 Codes
Hospital discharge data powered by ICD-10 codes plays a significant role in:
- Setting benchmarks for AAA repair procedures
- Identifying high-performing facilities
- Guiding quality improvement efforts
- Supporting research initiatives
- Shaping healthcare policies
Impact of ICD-10 Codes on Medicare and Private Insurers
Medicare and private insurers rely on these codes for various purposes, including:
- Calculating risk-adjusted payments
- Determining coverage decisions
- Evaluating provider performance
- Assessing treatment effectiveness
- Monitoring healthcare costs
Benefits of Accurate Coding Practices for Hospitals
Hospitals that implement accurate coding practices can expect to see several benefits, such as:
- Higher reimbursement rates
- Fewer claim rejections
- Better quality scores
- Improved compliance ratings
- Enhanced data reporting
Conclusion
The Top 7 Critical Facts About Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 shape the backbone of accurate medical coding practices.
These key facts empower healthcare providers to:
- Master specific diagnosis codes like I71.40
- Navigate the evolving ICD-10 classification system
- Document clinical details with precision
- Handle complex endovascular procedures
- Secure proper reimbursement
The journey through AAA coding reveals its vital role in patient care quality tracking and billing compliance. Understanding these codes helps medical teams focus on delivering excellent care while maintaining accurate records.
The medical coding landscape keeps changing. Healthcare providers who stay current with ICD-10 updates position themselves for success in both patient care and administrative tasks.
Remember: Precise coding isn’t just about numbers – it’s about ensuring patients receive proper care while healthcare facilities maintain their financial health.
Your mastery of AAA ICD-10 coding serves as a bridge between clinical excellence and operational success.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the ICD-10 code for abdominal aortic aneurysm without rupture and why is it important?
The ICD-10 code for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) without rupture is I71.40. Using this specific code is crucial for accurate billing, clinical records, and ensuring proper treatment documentation.
How has the ICD-10 code I71.4 for AAA without rupture evolved over time?
The I71.4 code transitioned over the years and will convert to a parent code in the 2024 and 2025 ICD-10 versions, impacting coding practices by requiring updates to maintain compliance and accuracy.
Where are aortic aneurysm codes like AAA classified within the ICD-10 system?
Aortic aneurysm codes, including those for abdominal aortic aneurysm, are categorized under diseases of the circulatory system in the ICD-10 classification system, specifically addressing aortic aneurysm and dissection.
Why is detailed coding with specific sub-codes such as I71.43 for infrarenal AAA important?
Detailed coding using specific sub-codes like I71.43 for infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm allows precise documentation of the aneurysm’s type and location, which enhances clinical accuracy and supports appropriate patient care and reimbursement.
What are the coding considerations for endovascular repair procedures of AAA, particularly fenestrated endovascular graft repairs?
Endovascular repair procedures for AAA require distinct coding considerations to accurately reflect the complexity of treatments such as fenestrated endovascular graft repairs, ensuring proper clinical documentation and billing.
How do clinical documentation elements like rupture status, aneurysm location, size, and type affect accurate ICD-10 coding for AAA?
Essential clinical documentation elements including rupture status, aneurysm location, size, and type directly impact ICD-10 coding accuracy by providing necessary detail that guides precise code assignment critical for treatment tracking and reimbursement.

Pingback: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ICD-10: Understanding the Condition and Its Coding – sturmweg
Pingback: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and ICD-10 Classification: Understanding, Diagnosis, and Managementv – treibkrafti
Pingback: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Its ICD-10 Classification: A Comprehensive Overview – wunderiq
Pingback: Scoop Discounts At Priceline Pharmacy: Save Big On Ravisher And Health
Pingback: Panic Attack ICD 10 Codes Explained: Diagnosis, Classification
Pingback: 3 Alarming Trends Linked to the f43.10 diagnosis code in 2025