What kind of diseases does the ENT department treat?
Many people have questions: what diseases can the ENT department treat?
What is ENT?
The eyes, ears, mouth, nose, and throat are related and easily influence each other. Therefore, in the past, they were collectively referred to as ENT. With the advancement and development of science and technology, various medical disciplines have penetrated and promoted each other, expanding the scope of ENT. The ENT department was then divided into ophthalmology, otolaryngology, and dentistry. Among them, large hospitals with conditions further divided otolaryngology into ear, nose, and throat and head and neck surgery .
The emergence of further subdivisions such as ear microsurgery , ear neurosurgery , skull base surgery , audiology and balance science, nasal endoscopic surgery , nasal neurosurgery (nasal skull base surgery), head and neck surgery, laryngeal microsurgery , voice and speech diseases , and pediatric otolaryngology has greatly enriched the content of otolaryngology.
Therefore, ENT is actually a broad discipline that covers all diseases of the eyes, ears, nose, throat, skull base and neck. For example, the well-known thyroid lesions, pituitary tumors, parotid gland lesions, etc., as well as all diseases inside and outside the neck, also belong to the category of ENT. In terms of surgical treatment, otolaryngology and head and neck surgery has certain advantages.
Nowadays, the term “ENT department” has been abolished in comprehensive hospitals. The most familiar departments in hospitals are: Ophthalmology, Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, and Dentistry. However, in some small hospitals or outpatient clinics, for the convenience of patients, ophthalmology and ENT departments are often grouped together, but the name “ENT department” is still used.
Because ophthalmology in the ENT department has long been separated and the scope of diagnosis and treatment of ophthalmic diseases is clear, it will not be described specifically here. The ENT department covers the otolaryngology and head and neck part, which is a “battlefield”. It is a broad and multi-disciplinary subject that has intersections with general internal medicine, general surgery, pediatrics, and even traditional Chinese medicine.
If I have a cold, which department should I see?
Colds, sore throats, upper respiratory tract infections, etc., everyone’s first impression is that these are internal medicine diseases, but in fact they also involve otolaryngology: acute rhinitis, sinusitis , acute pharyngitis, tonsillitis, etc., which are all upper respiratory tract diseases and nasopharyngeal diseases. They can be seen by internal medicine and otolaryngology. The two do not conflict, and the two departments can complement each other.
For example, when coughing or expectoration occurs, the conventional thinking is to focus on internal medicine. However, if the initial symptoms occur in the throat, comprehensive consideration is still required:
1. Problems in the upper part of the throat are related to the nose: for example, sinusitis and postnasal drip can lead to postnasal drip syndrome , which can cause coughing and sputum production.
2. Downward flow of the throat is a problem of bronchial or gastroesophageal reflux in the lungs, which can also cause coughing and sputum;

3. Problems with the throat itself, such as allergic pharyngitis, inflammation of the throat cavity or throat tumors, etc., may cause coughing and sputum.

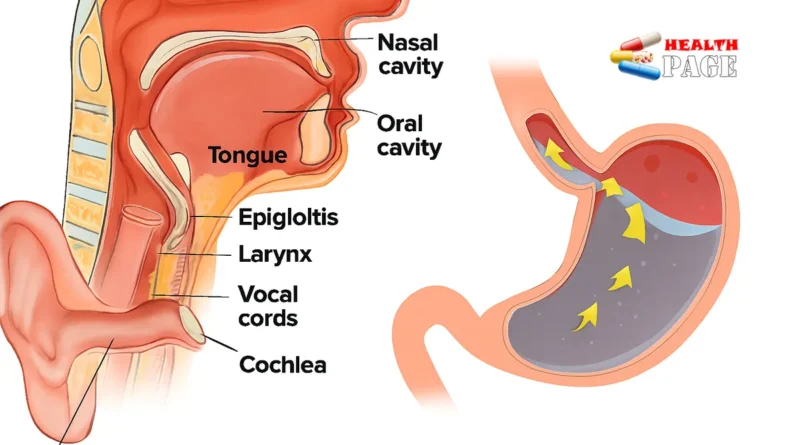
Because the nasopharyngeal cavity is an open channel, the symptoms it manifests often involve multiple causes. It is necessary to find the root cause in order to better treat it. Therefore, nasopharyngeal endoscopy examination is very necessary.
If I have a foreign body sensation in my throat, which department should I see?
For symptoms of the throat such as dry throat, throat discomfort, and foreign body sensation in the throat, you can see an internal medicine doctor, an otolaryngologist, or a traditional Chinese medicine doctor. It is best to do a laryngoscopy first. If problems with the throat itself (throat tumors, etc.) are ruled out, do not blindly use antibiotics. You can ask an internal medicine doctor or a traditional Chinese medicine doctor for assistance in diagnosis and treatment. The internal medicine doctor can see if there are any gastroesophageal reflux factors, and the traditional Chinese medicine doctor can use traditional Chinese medicine for conditioning. For chronic diseases, traditional Chinese medicine is indeed a good choice.
Which department should children go to for nose bleeding?
If children have purulent nasal discharge, foul-smelling nose, nosebleeds, or breathe with their mouths open, snore while sleeping, etc., it is natural that they are classified as pediatrics because they are children. However, because they are nasal problems, they can also be considered ENT diseases. The two departments can cooperate with each other. Pediatrics has more experience in the use of medication for children, while ENT has more advantages in the examination and treatment of the nose.
For those who do not see good results after taking the medicine, it is still necessary to do a nasal endoscopy to see if there is any foreign body in the nasal cavity, to identify the site of nasal bleeding, to identify the source of purulent nasal discharge, to see if there is any adenoid hypertrophy , to see if there is any deviated nasal septum , to see if there are any nasal polyps , to see if it is a cold, allergic rhinitis or sinusitis, and to further consider whether there are any other diseases such as blood diseases and then go to a specialist for treatment.
Which department should I see for deafness and tinnitus?
Deafness, tinnitus, etc. These symptoms may involve ENT, internal medicine, surgery, and traditional Chinese medicine, but ENT is the first choice. Why?
You should know that deafness alone can be divided into sensorineural deafness, conductive deafness, and mixed deafness. Tinnitus is also divided into corresponding types, including neurological tinnitus, conductive tinnitus, or psychogenic tinnitus. Some tinnitus and deafness are caused by earwax blockage or otitis media. As long as the earwax is removed, the symptoms will be relieved. If you blindly use drugs to dilate blood vessels or nourish nerves, it will easily cause a joke.

The ancients said, “There is a sequence in learning, and everyone has their own specialization in skills.”
Why do hospitals have to subdivide so many disciplines? Because the more specialized, the better. Professional content should be handled by specialists, and necessary examinations must be done. Where the first symptoms appear should be checked first, and only then can we make any further decisions.
At the same time, we must also have divergent thinking, a general practice concept, and comprehensive considerations. We cannot just focus on one part of the body when treating the disease. We must consider other factors in the whole body and promptly invite consultation assistance from other departments. Only in this way can we ensure that no one is missed in the diagnosis.

Pingback: The use of ventilator in clinical practice is a nightmare