How can you customize orthopedic shoes that are effective?
Orthopedic shoes, also known as corrective shoes. That are type of rehabilitation engineering auxiliary device used for foot and ankle correction treatment. They are make by professional doctors and rehabilitation engineering technicians base on the patient’s clinical signs and biomechanical test results. The guidance of clinical medicine and biomedical engineering theory, using orthopedic and shoemaking techniques to make a functional shoe.
Orthopedic shoes have a special structural design. Which use biomechanical means to apply corrective force to the foot and ankle to prevent and correct foot deformities. That treat and improve pain, lesions and joint instability caused by abnormal foot structure. The limit abnormal foot joint movement, compensate for the loss of foot function, delay and improve the occurrence and development of diseases. It promote the healthy development of children, and improve the quality of life of patients.
There are two common types of orthopedic shoes: customized personalized orthopedic shoes and finished orthopedic shoes. Foot and ankle orthopedic doctors formulate orthopedic prescriptions based on the patient’s symptoms, signs and auxiliary foot examination results, and choose appropriate orthopedic shoes for patients. Custom-made orthopedic shoes are designed and made according to the patient’s specific symptoms, test results, and foot data. They are more targeted to patients and have better functions. However, customized orthopedic shoes take a long time to make and are more expensive. Finished orthopedic shoes are made in batches, so they have lower costs and have the advantages of low price and fast speed. They have better effects on health care treatment for mild foot diseases and foot health.
Detail
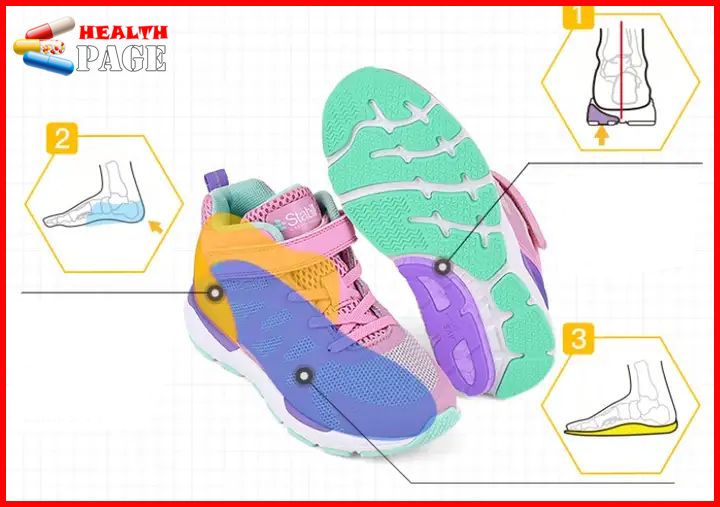
The upper consists of the forepart, the middle part of the shoe body, and the heel part. The upper structure consists of three parts: fabric, lining, and fixing strap.
Orthopedic shoe fabrics and linings are mostly made of natural leather. Which has the characteristics of good breathability, beauty, strength and durability. In recent years, some breathable chemical fiber and cloth fabrics have gradually increased in use. That due to their advantages of lightness, beauty, and rich colors.
The fixing straps of orthopedic shoes are divide into shoelaces and nylon Velcro. Traditional orthopedic shoes are mostly fixe by shoelaces. Which have the advantages of stable structure and firm fixation. But they are cumbersome to put on and take off when used. Nylon Velcro has the advantages of easy putting on and taking off, and the fixation is also firm, but the adhesion decreases after a period of use, and the fixing effect will be reduce.
The sole is compose of the outsole, midsole, and heel. The sole is roughly divide into the following types according to the style and material of the shoe;
Cowhide outsole: made of natural cowhide, strong, durable, and high cost.
Rubber outsole: made of natural rubber as the main material and adding a variety of ingredients, wear-resistant, non-slip, and slightly heavy.
EVA outsole: made of ethylene/vinyl acetate copolymer material as the main material and adding a variety of ingredients, light, soft, slightly poor wear resistance, and slightly poor anti-slip performance when exposed to water.
PU outsole: made of polyurethane, referred to as polyurethane, as the main material and adding a variety of ingredients, light, elastic, wear-resistant, but poor anti-slip performance when exposed to water.
The midsole of the shoe is make of cowhide, PHYLON, EVA, PU and other materials.
More Detail
Built-in orthotics in orthopedic shoes: mostly made of PP, PU, carbon fiber resin, leather pulp, chemical orthotics, hot melt adhesive orthotics and other materials. The built-in orthotics of finished orthopedic shoes are molded, and the built-in orthotics of custom-made orthopedic shoes need to be personalized according to the orthopedic prescription.
Special design of the sole and heel of orthopedic shoes
1) SACH heel: The back half of the heel is make of soft and elastic material to reduce the shock when the heel lands and relieve the ground reaction force borne by the heel and ankle joints.
2) Thomas heel: The inner side of the heel extends forward to the midfoot to support the medial longitudinal arch.
3) Reverse Thomas heel: The outer side of the heel extends forward to the midfoot to support the lateral longitudinal arch.
4) Wedge heel: Insert a wedge-shaped material on the inner or outer side of the heel to adjust the force line of the calcaneus.
5) Palm shaking: add arc-shaped horizontal bars to the metatarsal weight-bearing area to change the rolling axis of the foot.
6) Metatarsal horizontal bars: add flat-bottomed horizontal bars to the metatarsal weight-bearing area to change the pressure distribution on the sole of the foot.
7) Heightening: raise one sole to make up for the equal length of the lower limbs.
III. Styles of orthopedic shoes
Traditional styles are mostly lace-up styles, and the most common ones are Oxford style, Derby style, and Gibson style.
Modern styles
Modern styles have a wide range of choices. As long as they meet the design requirements of orthopedic prescriptions and can accommodate sufficient orthopedic space. they can be use as orthopedic shoe styles. Customiz personalized orthopedic shoes can be design according to the needs of patients.
IV. Prescription design of orthopedic shoes:
It is formulate by orthopedic doctors with rich clinical orthopedic treatment experience. They fully considers the type, stage and recovery of the patient’s disease, combine with the results of physical examination. Also clinical examination, and biomechanical examination of the foot, and then a comprehensive analysis is make. Orthopedic prescriptions should have a global concept, establish short-term. Also medium-term and long-term orthopedic goals, and coordinate with the different needs of clinical treatment and rehabilitation treatment. The design of orthopedic prescriptions should fully consider the difficulty of production. The aesthetics, comfort, cost-effectiveness, psychological impact of orthopedic shoes, and establish a good follow-up mechanism.
Data collection of orthopedic shoes:
1. Foot measurement: Use a soft ruler to directly measure data on the foot. The disadvantage is that the error is large and the repeatability is poor.
Plaster mold: Use a plaster bandage to make a negative mold on the foot, and then make a positive mold of the foot. The disadvantage is that the plaster negative mold is easy to deform, and the plaster shrinks and expands after solidification.
Foot mold box: Use a special foot template Form to take the mold, and then make a plaster positive mold. The disadvantage is that there is only sole data and the error is large.
Three-dimensional foot scanning: Use a special three-dimensional scanning device to accurately establish a digital three-dimensional model of the foot, which is convenient for data storage and has minimal error. The disadvantage is that the equipment is expensive and difficult to
Siix Common biomechanical testing methods for orthopedic shoes:
Pleat pressure test: A dedicated plantar pressure test system is use to test the plantar pressure of patients in static standing and dynamic walking. The force conditions of various parts of the sole of the foot at different periods are obtain. The results are quantitatively analyz to provide a reliable basis for diagnosis.



Pingback: Skechers Orthopedic Shoes: The Ultimate Guide for 2024