What are the common orthopedic diseases?
In this article we are going to discuss common orthopedic diseases. We know that an adult has 206 bones in the body, each with a certain shape and function. Bones are closely connected, and their shapes and functions are mutually restricted. When the structure and function of bones and joints are damage, varying degrees of limb dysfunction will occur, which will then lead to various bone diseases, causing varying degrees of impact on human health and life. So today we will focus on the common bone diseases in daily life. If you experience the following symptoms, please go to the hospital in time.
Frozen Shoulder
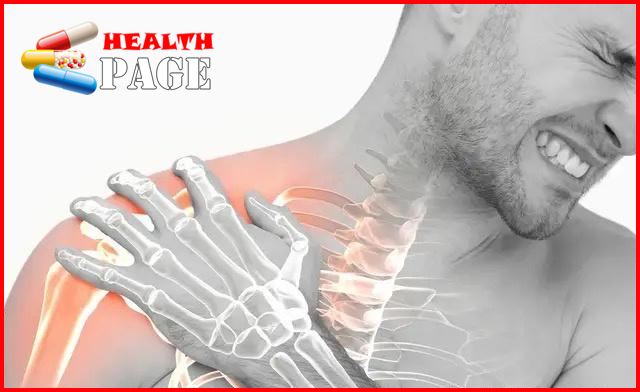
Periarthritis of the shoulder is abbreviated as frozen shoulder, commonly known as frozen shoulder or frozen shoulder. It is a chronic specific inflammation of the shoulder capsule and its surrounding ligaments, tendons and bursae, characterized by gradual onset of shoulder pain, especially at night, which gradually worsens and limits the function of the shoulder joint and worsens day by day. After reaching a certain level, it gradually eases until it is completely restored.
arthritis
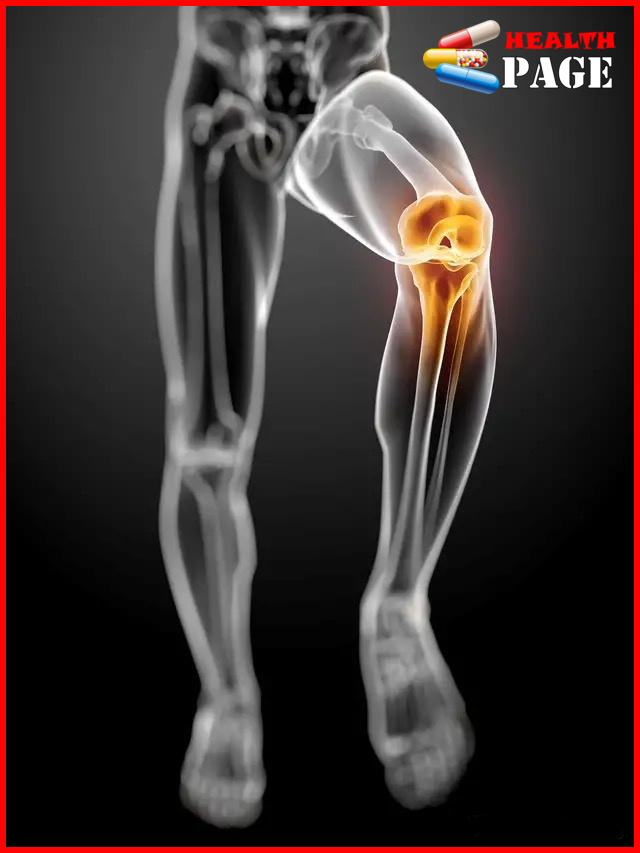
Arthritis refers to inflammatory diseases that occur in human joints and surrounding tissues. The causes of arthritis are complex, mainly related to factors such as inflammation, autoimmune response, infection, metabolic disorders, trauma, degenerative diseases, etc.; clinical manifestations are redness, swelling, heat, pain, dysfunction and joint deformity of the joints. Severe cases can lead to joint disability and bring a lot of inconvenience to the patient’s life; there are many types of arthritis, mainly rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gouty arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, infectious arthritis and others such as traumatic arthritis, nephrotic arthritis, etc.
Lumbar disc herniation
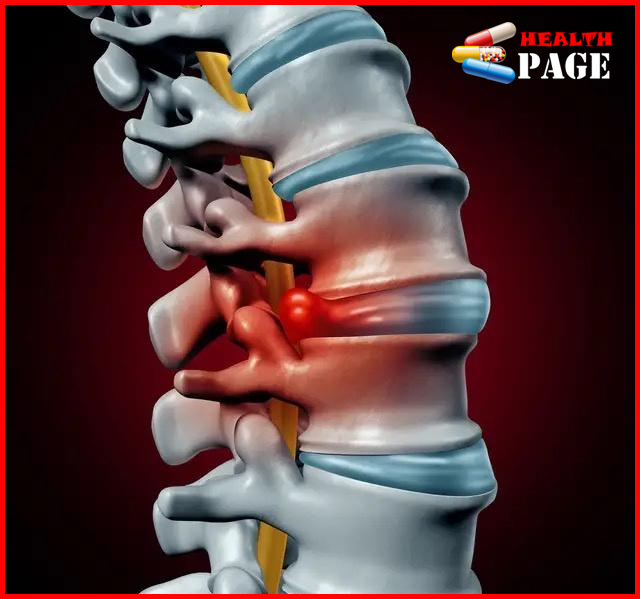
Lumbar disc herniation is one of the more common bone diseases, which can occur in the elderly, middle-aged and young. It is mainly cause by the degenerative changes of the various parts of the lumbar disc (nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus and cartilage plate), especially the nucleus pulposus, to varying degrees. Under the influence of external factors, the annulus fibrosus of the disc ruptures, and the nucleus pulposus tissue protrudes (or falls out) from the ruptured part to the back or inside the spinal canal, causing the adjacent spinal nerve roots to be stimulate or compress, resulting in a series of clinical symptoms such as low back pain, numbness and pain in one or both lower limbs. The highest incidence of this disease is in L4-5 and L5-S1, accounting for about 95%.
Cervical Spondylosis
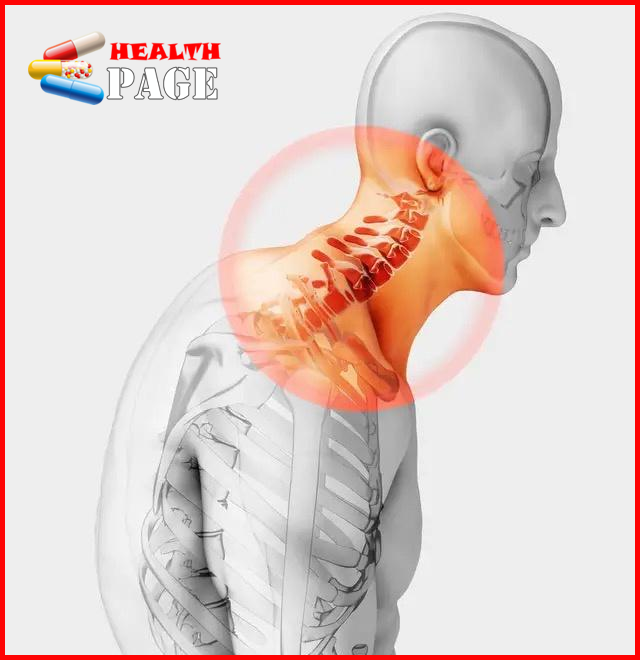
The general term for cervical osteoarthritis, hypertrophic cervical spondylitis, cervical radiculopathy and cervical disc herniation is a disease based on degenerative pathological changes. It is mainly cause by long-term strain of the cervical spine, bone hyperplasia, or disc herniation, ligament thickening, which leads to compression of the cervical spinal cord, nerve roots or vertebral arteries, resulting in a series of clinical syndromes of functional disorders, manifested as vertebral instability and loosening; protrusion or extrusion of the nucleus pulposus; bone spur formation; ligament hypertrophy and secondary spinal canal stenosis, etc., which stimulate or compress the adjacent nerve roots, spinal cord, vertebral arteries and cervical sympathetic nerves and other tissues, causing a series of symptoms and signs.
Ankylosing spondylitis
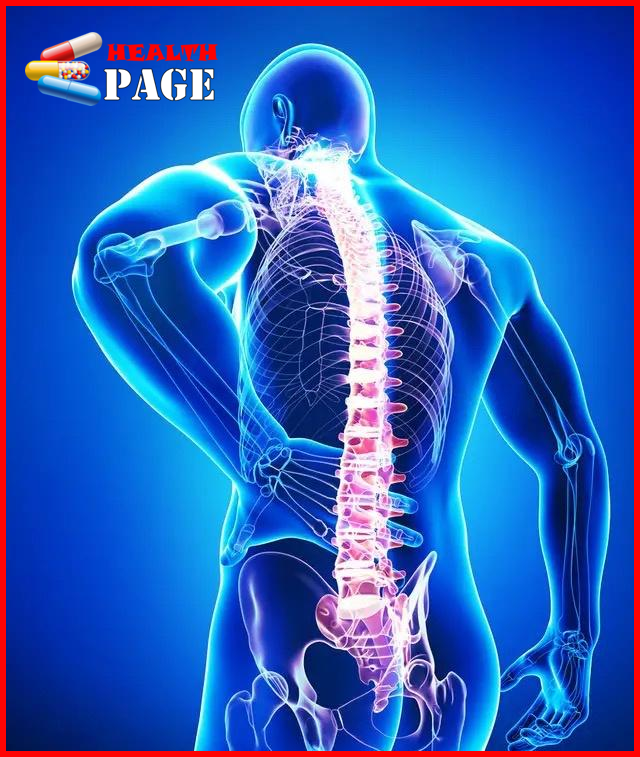
Ankylosing spondylitis belongs to the category of rheumatic diseases and is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy. The cause of the disease is still unclear. It is a chronic disease with the spine as the main lesion, involving the sacroiliac joints, causing spinal stiffness and fibrosis, and causing varying degrees of eye, lung, muscle, and bone lesions. It is an autoimmune disease.
Sciatica
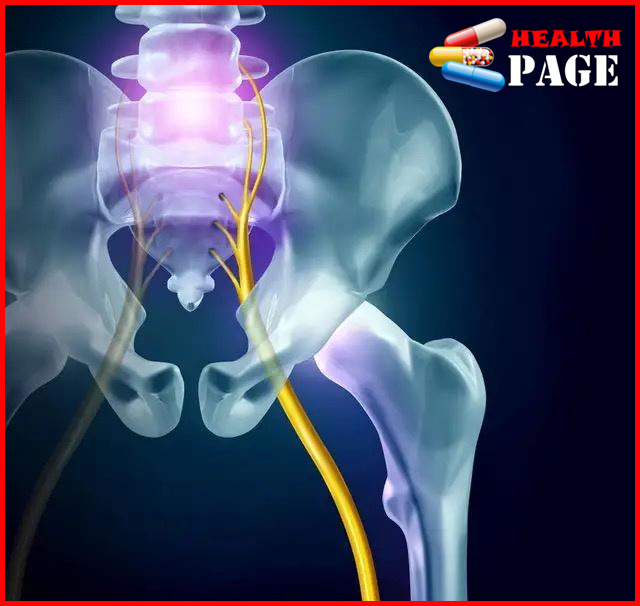
It is a syndrome characterize by pain in the sciatic nerve pathway and distribution area. The vast majority of sciatica cases are secondary to lesions in the local sciatic nerve and surrounding structures that cause stimulation, compression and damage to the sciatic nerve, which is call secondary sciatica. A few are primary, which is clinically know as sciatica.
Femoral head necrosis
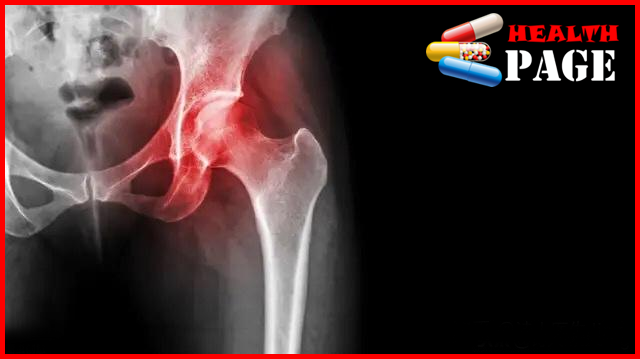
Femoral head necrosis is a pathological evolution process, which initially occurs in the weight-bearing area of the femoral head. Under the action of stress, the trabecular structure of the necrotic bone is damage, namely microfracture, and then the damage bone tissue is repaired. If the cause of bone necrosis is not eliminate and the repair is not perfect, the damage-repair process continues, leading to changes in the femoral head structure, femoral head collapse, deformation, joint inflammation, and dysfunction.
fracture
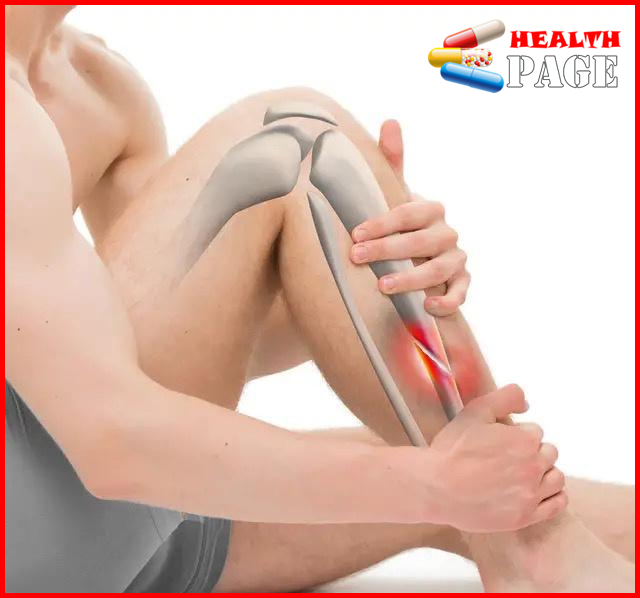
It refers to the complete or partial break of the continuity of the bone structure; it is more common in children and the elderly, and sometimes occurs in young and middle-aged people. Patients often have a fracture in one part, and a few have multiple fractures. The typical manifestations of fracture patients are local deformation after injury, abnormal movement of limbs, and bone friction sound when moving limbs; in addition, the wound is extremely painful, with local swelling and congestion, and movement disorders after injury. X-rays can show the location, shape and displacement of the fracture. For many elderly people, fractures caused by osteoporosis are relatively common.
gout
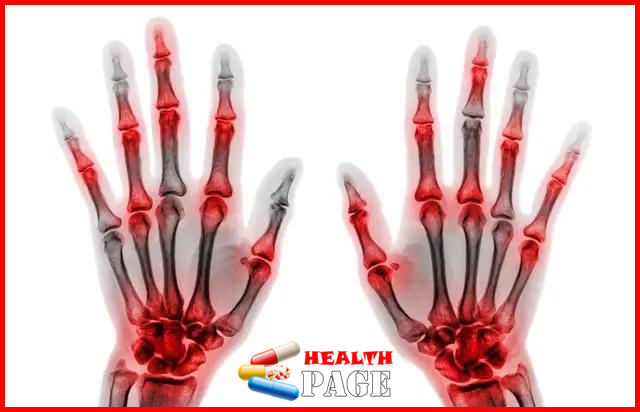
Gout is a crystal-related arthritis cause by the deposition of monosodium urate. Which is directly related to hyperuricemia caused by purine metabolism disorder and/or reduced uric acid excretion. It specifically refers to acute characteristic arthritis and chronic tophi disease, mainly including acute onset arthritis, tophi formation, etc. Patients often wake up in the middle of the night due to joint pain, which progressively intensifies, and the affected joints and surrounding tissues become red, swollen, hot, painful, and have limited function.

Pingback: Can teenagers safely use protein powder?
Pingback: Understanding CPT Code 27279: A Comprehensive Guide